社区微信群开通啦,扫一扫抢先加入社区官方微信群

社区微信群
社区微信群开通啦,扫一扫抢先加入社区官方微信群

社区微信群
Spring Data 提供了几个接口供继承使用,如 JpaRepository,另外还规定了方法查询中的关键字,即你命名的查询方法需要符合规范。
详情参考:SpringBoot整合Spring Data JPA、SpringDataJPA入门。
本篇博文详细记录Spring Data JPA查询中的那些事,尤其是复杂的动态查询。
① 只要符号命名规范的接口都可以被正常解析使用
find|read|get开头;_ 进行连接。如下所示:
//根据 lastName 来获取对应的 Person
Person getByLastName(String lastName);
//WHERE lastName LIKE ?% AND id < ?
List<Person> getByLastNameStartingWithAndIdLessThan(String lastName, Integer id);
//WHERE lastName LIKE %? AND id < ?
List<Person> getByLastNameEndingWithAndIdLessThan(String lastName, Integer id);
//WHERE email IN (?, ?, ?) OR birth < ?
List<Person> getByEmailInAndBirthLessThan(List<String> emails, Date birth);
② 支持级联查询
如User类中有属性为Address类。
User类如下:
@Entity //告诉JPA这是一个实体类(和数据表映射的类)
@Table(name = "tb_user") //@Table来指定和哪个数据表对应;如果省略默认表名就是user;
public class User implements Serializable{
@Id //这是一个主键
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)//自增主键
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "last_name",length = 50) //这是和数据表对应的一个列
private String lastName;
@Column //省略默认列名就是属性名
private String email;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "address_id")
private Address address;
//...
}
UserRepository中添加方法如下:
List<User> getByAddressIdGreaterThan(Integer id);
进行测试,查看控制台打印SQL:
SELECT
user0_.id AS id1_1_,
user0_.address_id AS address_4_1_,
user0_.email AS email2_1_,
user0_.last_name AS last_nam3_1_
FROM
tb_user user0_
LEFT OUTER JOIN tb_address address1_ ON user0_.address_id = address1_.id
WHERE
address1_.id >?
其默认使用左外连接对tb_address表进行级联查询,根据tb_address表的id进行判断。
③ 如果User中有个自身属性为addressId,怎么处理?
User如下所示:
@Entity //告诉JPA这是一个实体类(和数据表映射的类)
@Table(name = "tb_user") //@Table来指定和哪个数据表对应;如果省略默认表名就是user;
public class User implements Serializable{
@Id //这是一个主键
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)//自增主键
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "last_name",length = 50) //这是和数据表对应的一个列
private String lastName;
@Column //省略默认列名就是属性名
private String email;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "address_id")
private Address address;
@Column(name = "add_id")
private int addressId;
//...
}
此时再次测试接口方法:
List<User> getByAddressIdGreaterThan(Integer id);
查看控制台打印SQL:
SELECT
user0_.id AS id1_1_,
user0_.address_id AS address_5_1_,
user0_.add_id AS add_id2_1_,
user0_.email AS email3_1_,
user0_.last_name AS last_nam4_1_
FROM
tb_user user0_
WHERE
user0_.add_id >?
默认直接使用tb_user表的add_id(即User的私有addressId属性)进行查询!
那么此时还想根据Address.id进行查询怎么办?
若当前类有符合条件的属性时,优先使用当前类自身属性而不使用级联属性。若想使用级联属性,则属性之间用 _ 进行连接。
如下所示:
//WHERE a.id > ?
List<User> getByAddress_IdGreaterThan(Integer id);
查看控制台打印SQL:
SELECT
user0_.id AS id1_1_,
user0_.address_id AS address_5_1_,
user0_.add_id AS add_id2_1_,
user0_.email AS email3_1_,
user0_.last_name AS last_nam4_1_
FROM
tb_user user0_
LEFT OUTER JOIN tb_address address1_ ON user0_.address_id = address1_.id
WHERE
address1_.id >?
使用左外连接对tb_address表进行级联查询,根据tb_address表的id进行判断。
如果查询接口不符合命名规范呢,如果想使用自定义查询,比如子查询呢?
上面所讲述的方法将失效,此时就要用到@Query注解,注解里面使用JPQL语言或者普通SQL查询。
① 使用JPQL
关于JPQL参考博文:JPQL语言和Query接口、JPQL查询实例。
如下所示,查询id最大的用户:
@Query("select u from User u where u.id=(select max(u2.id)
from User u2)")
User getMaxIdPerson(Integer id);
查看控制台打印SQL如下:
SELECT
user0_.id AS id1_1_,
user0_.address_id AS address_5_1_,
user0_.add_id AS add_id2_1_,
user0_.email AS email3_1_,
user0_.last_name AS last_nam4_1_
FROM
tb_user user0_
WHERE
user0_.id = (
SELECT
max(user1_.id)
FROM
tb_user user1_
)
② JPQL参数传递
怎么往@Query注解中的JPQL中传递参数呢?两种方式:索引参数和命名参数。
索引参数如下所示,索引值从1开始,查询中 ”?X”个数需要与方法定义的参数个数相一致,并且顺序也要一致。
实例如下:
@Query("select u from User u where u.lastName=?1 and u.email=?2")
User testQueryAnnotationParams1(String lastName,String email);
查看控制台打印SQL如下:
SELECT
user0_.id AS id1_1_,
user0_.address_id AS address_5_1_,
user0_.add_id AS add_id2_1_,
user0_.email AS email3_1_,
user0_.last_name AS last_nam4_1_
FROM
tb_user user0_
WHERE
user0_.last_name =?
AND user0_.email =?
可以定义好参数名,赋值时采用@Param(“参数名”),而不用管顺序。推荐使用这种方式。
实例如下:
@Query("select u from User u where u.lastName=:lastName and u.email=:email")
User testQueryAnnotationParams2(@Param("lastName") String lastName, @Param("email") String email);
查看控制台打印SQL如下:
SELECT
user0_.id AS id1_1_,
user0_.address_id AS address_5_1_,
user0_.add_id AS add_id2_1_,
user0_.email AS email3_1_,
user0_.last_name AS last_nam4_1_
FROM
tb_user user0_
WHERE
user0_.last_name =?
AND user0_.email =?
命名参数对比索引参数,其使用起来并没有什么大的差别。但是还是推荐在自定义使用JPQL查询时,使用命名参数,参数名一一对应,不容易混淆。
注意:如果使用命名参数,方法参数处必须使用@Param指定参数名!
③ Query中有like关键字
如果是 @Query 中有 LIKE 关键字,后面的参数需要前面或者后面加 %,这样在传递参数值的时候就可以不加 %:
//参数后面添加%
@Query("select u from User u where u.lastName like ?1%")
public List<User> findBylastName (String lastName );
//参数前面添加%
@Query("select u from User u where u.lastName like %?1")
public List<User> findBylastName (String lastName );
//参数前后添加%
@Query("select u from User u where u.lastName like %?1%")
public List<User> findBylastName (String lastName );
这里以参数后面添加%为例,查询控制台打印SQL如下所示:
SELECT
user0_.id AS id1_1_,
user0_.address_id AS address_5_1_,
user0_.add_id AS add_id2_1_,
user0_.email AS email3_1_,
user0_.last_name AS last_nam4_1_
FROM
tb_user user0_
WHERE
user0_.last_name LIKE ?
其实也可以不在@Query中写%,而是传参过来。但是我想,你不会喜欢在参数中添加%的!
④ Native Query
就是想使用原生SQL查询怎么做?SpringData同样支持!
可以使用@Query来指定本地查询,只要设置nativeQuery为true。
示例如下:
@Query(nativeQuery = true,value = "select count(1) from tb_user")
long getTotalCount();
控制台打印SQL如下:
Hibernate: select count(1) from tb_user
可以通过自定义的JPQL完成update和delete操作,JPQL不支持insert操作。
在@Query中编写JPQL语句进行update或者delete时,必须使用@Modifying注解,以通知SpringData这是一个update或者delete操作。
在update或者delete操作时,需要使用事务;此时需要在Service实现类的方法上声明事务@Transactional。
① @Query 与 @Modifying 执行更新操作
@Query 与 @Modifying 这两个 annotation一起声明,可定义个性化更新操作,例如只涉及某些字段更新时最为常用。
接口方法如下:
@Query("update User u set u.email = :email where u.id = :id")
int updateEmailById(@Param("id") Integer id,@Param("email") String email);
尝试进行操作抛异常:
org.hibernate.hql.internal.QueryExecutionRequestException:
Not supported for DML operations [update com.jane.model.User u
set u.email = :email where u.id = :id]
意思是说不支持的数据库操作,关于DML科普如下:
DML(data manipulation language)数据操纵语言:就是我们最经常用到的 SELECT、UPDATE、INSERT、DELETE。 主要用来对数据库的数据进行一些操作
.
DDL(data definition language)数据库定义语言:其实就是我们在创建表的时候用到的一些sql,比如说:CREATE、ALTER、DROP等。DDL主要是用在定义或改变表的结构,数据类型,表之间的链接和约束等初始化工作上。
.
DCL(Data Control Language)数据库控制语言:是用来设置或更改数据库用户或角色权限的语句,包括(grant,deny,revoke等)语句。
@Modifying
@Query("update User u set u.email = :email where u.id = :id")
int updateEmailById(@Param("id") Integer id,@Param("email") String email);
再次测试如下:
javax.persistence.TransactionRequiredException:
Executing an update/delete query
意思是说执行update或者delete操作时,必须显示声明事务!
② 事务
Spring Data 提供了默认的事务处理方式,即所有的查询均声明为只读事务。
对于自定义的方法,如需改变 Spring Data 提供的事务默认方式,可以在方法上注解 @Transactional 声明 。
进行多个 Repository 操作时,也应该使它们在同一个事务中处理,按照分层架构的思想,这部分属于业务逻辑层,因此,需要在 Service 层实现对多个 Repository 的调用,并在相应的方法上声明事务。
Service实现类如下:
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserServcie{
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepository;
@Transactional//这里声明事务
public int updateEmailById(Integer id, String email) {
System.out.println("进入Service方法。。。");
int i = userRepository.updateEmailById(id, email);
return i;
}
}
查询控制台打印SQL如下:
Hibernate: update tb_user set email=? where id=?
在以前项目中 @Transactional一般是放在Service接口中的,并非实现类中。但是在这里放在接口中不行仍然抛出上面那个需要事务的异常。
PagingAndSortingRepository接口继承自CrudRepository,在此基础上添加了两个方法:
//根据Sort返回排序后的集合
Iterable<T> findAll(Sort sort);
//根据Pageable对象返回 a Page of entities
Page<T> findAll(Pageable pageable);
通常我们使用Page<T> findAll(Pageable pageable);来进行分页。
① Pageable是什么
这货是一个接口,封装了分页的相关操作,源码如下:
public interface Pageable {
/**
* Returns a {@link Pageable} instance representing no pagination setup.
*/
static Pageable unpaged() {
return Unpaged.INSTANCE;
}
/**
* Returns whether the current {@link Pageable} contains pagination information.
*/
default boolean isPaged() {
return true;
}
/**
* Returns whether the current {@link Pageable} does not contain pagination information.
*/
default boolean isUnpaged() {
return !isPaged();
}
//pageNumber
int getPageNumber();
//pageSize
int getPageSize();
/**
* Returns the offset to be taken according to the underlying page and page size.
*/
long getOffset();
/**
* Returns the sorting parameters.
*/
Sort getSort();
/**
* Returns the current {@link Sort} or the given one if the current one is unsorted.
*
* @param sort must not be {@literal null}.
*/
default Sort getSortOr(Sort sort) {
Assert.notNull(sort, "Fallback Sort must not be null!");
return getSort().isSorted() ? getSort() : sort;
}
/**
* Returns the {@link Pageable} requesting the next {@link Page}.
*/
Pageable next();
/**
* Returns the previous {@link Pageable} or the first {@link Pageable} if the current one already is the first one.
*/
Pageable previousOrFirst();
/**
* Returns the {@link Pageable} requesting the first page.
*/
Pageable first();
/**
* Returns whether there's a previous {@link Pageable} we can access from the current one. Will return
* {@literal false} in case the current {@link Pageable} already refers to the first page.
*
* @return
*/
boolean hasPrevious();
/**
* Returns an {@link Optional} so that it can easily be mapped on.
*
* @return
*/
default Optional<Pageable> toOptional() {
return isUnpaged() ? Optional.empty() : Optional.of(this);
}
}
通常我们并不会实现该接口来进行分页,而是使用其实现类PageRequest来进行分页操作。
其构造函数如下:
//最简单的分页
public PageRequest(int page, int size) {}
// 分页+排序
public PageRequest(int page, int size, Sort sort) {};
//分页+排序=》不使用sort,直接提供direction和properties
public PageRequest(int page, int size, Direction direction,
String... properties) {};
在SpringBoot2.0下,这些构造方法已经过时,SpringBoot2.0建议我们使用其静态方法创建对象:
// 最简单的分页
public static PageRequest of(int page, int size) {
return of(page, size, Sort.unsorted());
}
// 分页+排序
public static PageRequest of(int page, int size, Sort sort) {
return new PageRequest(page, size, sort);
}
//分页+排序=》不使用sort,直接提供direction和properties
public static PageRequest of(int page, int size, Direction direction, String... properties) {
return of(page, size, Sort.by(direction, properties));
}
其实关于第三种方法,可以查看源码得知其和第二种方法并无差异!唯一的区别是使用第二种方式创建sort时可以不用指定ASC|DESC,但是使用第三种方法Direction不能为null !!
② 分页实例
Controller测试如下:
@GetMapping("/test12")
public Page<User> test12(){
int page = 1;//当前页,从 0 开始。
int pageSize = 5;
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(page,pageSize);
Page<User> userPage = userRepository.findAll(pageable);
return userPage;
}
返回结果如下:
content里面的数据如图右侧所示。分页查询结果可谓是很详细了!!
查看控制台SQL打印:
SELECT
user0_.id AS id1_1_,
user0_.address_id AS address_5_1_,
user0_.add_id AS add_id2_1_,
user0_.email AS email3_1_,
user0_.last_name AS last_nam4_1_
FROM
tb_user user0_
LIMIT ?, ?
//...
底层SQL还是我们熟悉的limit !
③ 分页排序实例
功能:如按照id倒序分页。
Controller实例如下:
@GetMapping("/test13")
public Page<User> test13(){
Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC,"id");
int page = 1;
int pageSize = 5;
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(page,pageSize,sort);
Page<User> userPage = userRepository.findAll(pageable);
return userPage;
}
Sort是为查询进行排序服务的,至少应该提供一个排序熟悉,默认排序为ASC,可以通过其静态内部枚举类Direction进行制定。Sort源码如下:
/**
* Sort option for queries. You have to provide at least a list of properties to sort for that must not include
* {@literal null} or empty strings. The direction defaults to {@link Sort#DEFAULT_DIRECTION}.
*
* @author Oliver Gierke
* @author Thomas Darimont
* @author Mark Paluch
*/
public class Sort implements Streamable<org.springframework.data.domain.Sort.Order>, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5737186511678863905L;
private static final Sort UNSORTED = Sort.by(new Order[0]);
public static final Direction DEFAULT_DIRECTION = Direction.ASC;
//...
}
查看控制台SQL打印:
SELECT
user0_.id AS id1_1_,
user0_.address_id AS address_5_1_,
user0_.add_id AS add_id2_1_,
user0_.email AS email3_1_,
user0_.last_name AS last_nam4_1_
FROM
tb_user user0_
ORDER BY
user0_.id DESC
LIMIT ?, ?
查看页面返回分页排序结果:
相关介绍参考:Spring Data JPA入门简解。
此时让UserRepository继承自JpaSpecificationExecutor,如下:
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User,Integer>,JpaSpecificationExecutor<User> {
//...
}
额外注意一点,Java中类是单继承,接口是可以多继承的。
Controller实例如下:
/**
* 目标: 实现带查询条件的分页. id > 5 的条件
*
* 调用 JpaSpecificationExecutor 的 Page<T> findAll(Specification<T> spec, Pageable pageable);
* Specification: 封装了 JPA Criteria 查询的查询条件
* Pageable: 封装了请求分页的信息: 例如 pageNo, pageSize, Sort
*/
@GetMapping("/test15")
public Page<User> test15(){
Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC,"id");
int page = 1;
int pageSize = 5;
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(page,pageSize,sort);
//通常使用 Specification 的匿名内部类
Specification<User> specification = new Specification<User>() {
/**
* @param *root: 代表查询的实体类.
* @param query: 可以从中得到 Root 对象,
* 即告知 JPA Criteria 查询要查询哪一个实体类.
* 还可以来添加查询条件, 还可以结合 EntityManager 对象得到最终查询的 TypedQuery 对象.
* @param *cb: CriteriaBuilder 对象.
* 用于创建 Criteria 相关对象的工厂.
* 当然可以从中获取到 Predicate 对象
* @return: *Predicate 类型, 代表一个查询条件.
*/
@Override
public Predicate toPredicate(Root<User> root,
CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb) {
Path path = root.get("id");
Predicate predicate = cb.gt(path, 5);
return predicate;
}
};
Page<User> userPage = userRepository.findAll(specification, pageable);
return userPage;
}
页面返回结果如下所示:
其中totalElements:22;totalPages:5。说明已经过滤了id小于等于5的实体!
查看控制台打印SQL如下:
SELECT
user0_.id AS id1_1_,
user0_.address_id AS address_5_1_,
user0_.add_id AS add_id2_1_,
user0_.email AS email3_1_,
user0_.last_name AS last_nam4_1_
FROM
tb_user user0_
WHERE
user0_.id > 5
ORDER BY
user0_.id DESC
LIMIT ?, ?
支持,使用JpaSpecificationExecutor完成了一个动态查询。下面详细研究一下相关联的几个接口和类。
首先传参为Specification,其内部封装了Predicate,如下所示:
/**
* Creates a WHERE clause for a query of the referenced entity in form of a {@link Predicate} for the given
* {@link Root} and {@link CriteriaQuery}.
*
* @param root must not be {@literal null}.
* @param query must not be {@literal null}.
* @param criteriaBuilder must not be {@literal null}.
* @return a {@link Predicate}, may be {@literal null}.
*/
@Nullable
Predicate toPredicate(Root<T> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder criteriaBuilder);
//使用给定的root,query&criteriaBuilder返回一个where子句---即一个查询条件
通常使用匿名类的方式并实现toPredicate方法来达到实现复杂动态查询的目的。
Root接口如下:
/**
* A root type in the from clause.
* // From字句中的根类型
* Query roots always reference entities.
* //查询根总是引用实体
*
* @param <X> the entity type referenced by the root//X为根引用的实体类型
* @since Java Persistence 2.0
*/
public interface Root<X> extends From<X, X> {
/**
* // 返回与根(ROOT)对应的元模型实体
* @return metamodel entity corresponding to the root
*/
EntityType<X> getModel();
}
可以简单理解Root为代表查询的实体类。其接口继承示意图如下: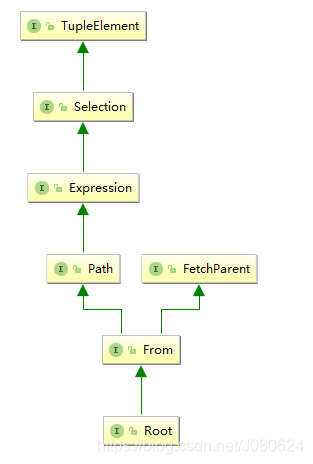
ROOT接口实现类继承示意图如下: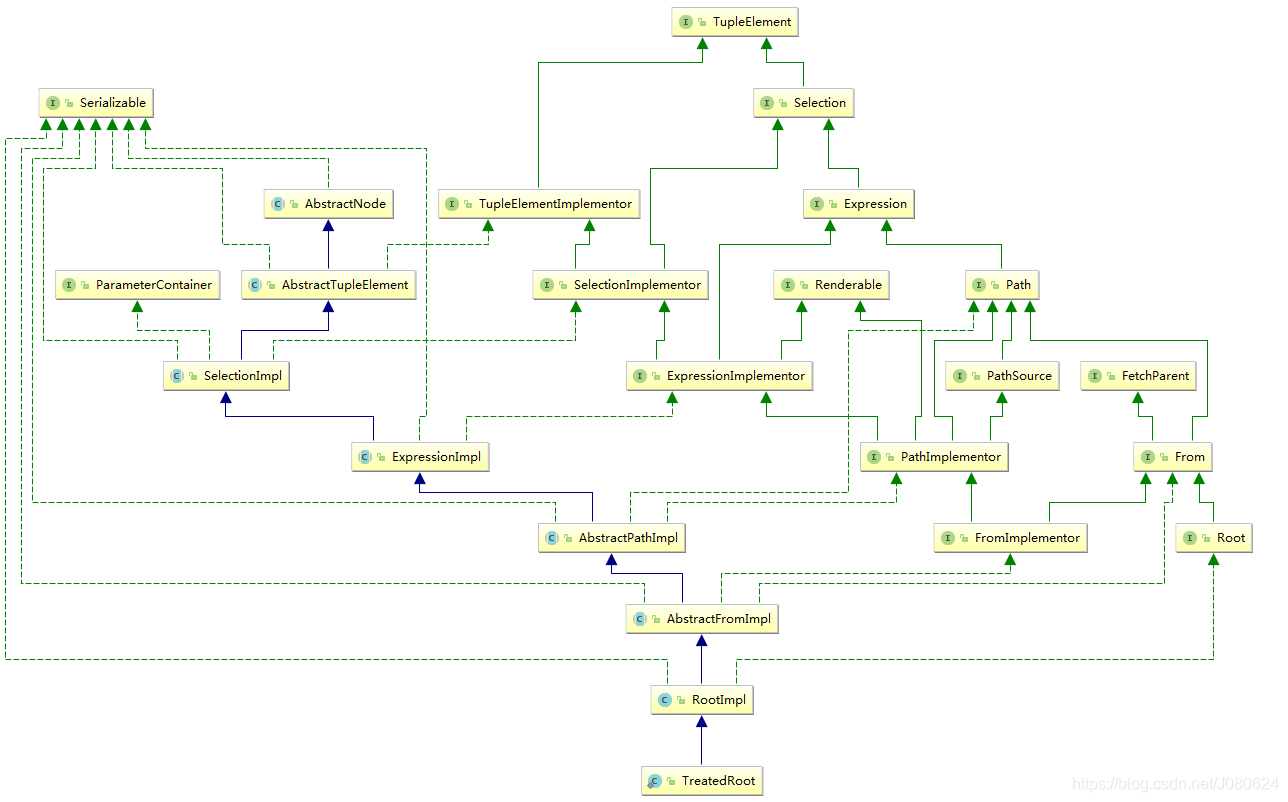
TreatedRoot是RootImpl静态内部子类,如下所示;
public static class TreatedRoot<T> extends RootImpl<T> {
private final RootImpl<? super T> original;
private final Class<T> treatAsType;
public TreatedRoot(RootImpl<? super T> original, Class<T> treatAsType) {
super(
original.criteriaBuilder(),
original.criteriaBuilder().getEntityManagerFactory().getMetamodel().entity( treatAsType )
);
this.original = original;
this.treatAsType = treatAsType;
}
//...
}
本例中ROOT具体如下: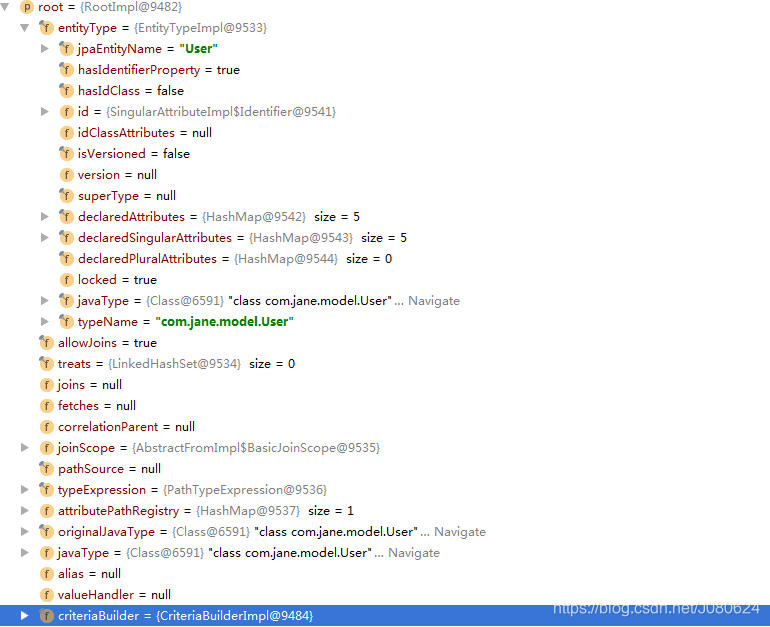
CriteriaQuery
该接口定义了一些具体的、功能性的方法(对于那些顶层查询来讲)。代表一个specific的顶层查询对象,它包含着查询的各个部分,比如:select 、from、where、group by、order by。
其主要方法如下:
本实例中CriteriaQuery如下所示: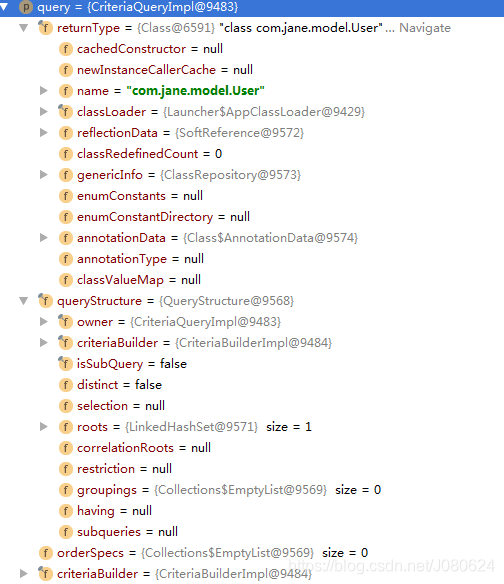
CriteriaBuilder接口
该接口用于构造criteria queries, compound selections,expressions, predicates, orderings。
其下面有很多方法:
Predicate接口(代表一个简单或复杂的查询条件)
代表Criteria查询的根对象,定义了实体类型,能为将来导航获得想要的结果。
源码如下:
/**
* The type of a simple or compound predicate: a conjunction or
* disjunction of restrictions.--And || OR
* A simple predicate is considered to be a conjunction with a
* single conjunct.
*
* @since Java Persistence 2.0
*/
public interface Predicate extends Expression<Boolean> {
public static enum BooleanOperator {
AND,
OR
}
/**
* Return the boolean operator for the predicate.
* If the predicate is simple, this is <code>AND</code>.
*
* @return boolean operator for the predicate
*/
BooleanOperator getOperator();
/**
* Whether the predicate has been created from another
* predicate by applying the <code>Predicate.not()</code> method
* or the <code>CriteriaBuilder.not()</code> method.
*
* @return boolean indicating if the predicate is
* a negated predicate
*/
boolean isNegated();
/**
* Return the top-level conjuncts or disjuncts of the predicate.
* Returns empty list if there are no top-level conjuncts or
* disjuncts of the predicate.
* Modifications to the list do not affect the query.
*
* @return list of boolean expressions forming the predicate
*/
List<Expression<Boolean>> getExpressions();
// 创建一个否定的(反面的)Predicate
Predicate not();
}
接口继承示意图如下: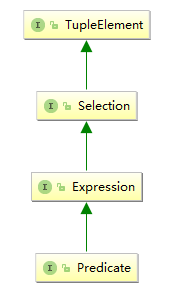
本实例中Predicate具体如下: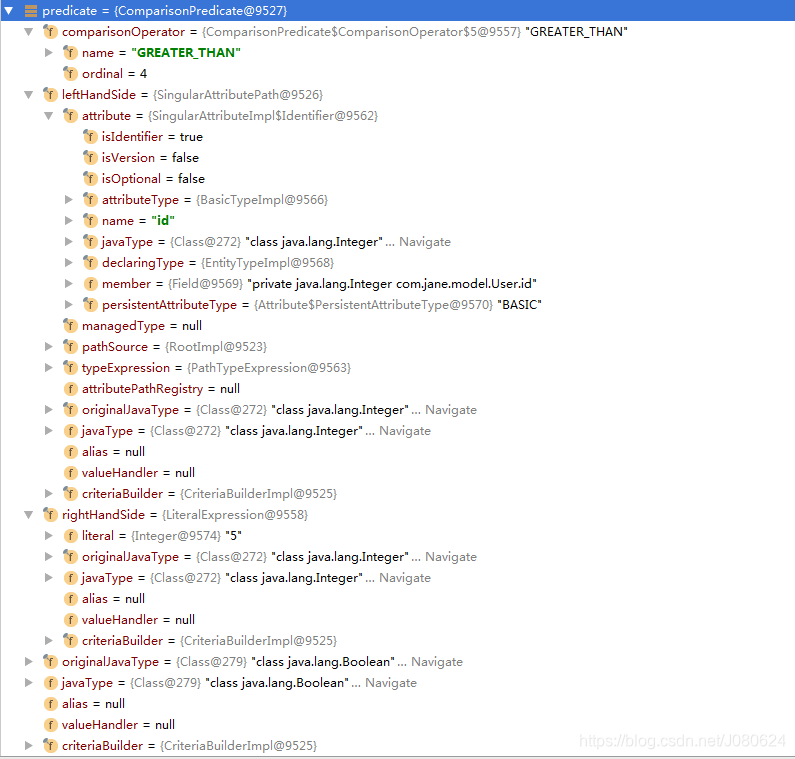
即 左边&操作符&右边==》leftHandSide&comparisonOperator&rightHandSide,可以把它当做一个Expression。
两个层次:为某一个 Repository 上添加自定义方法;为所有的 Repository 都添加自实现的方法。
① 为某一个 Repository 上添加自定义方法
步骤如下:
即如下图所示:
注意: 默认情况下, Spring Data 会在 base-package 中查找 “接口名Impl” 作为实现类。也可以通过repository-impl-postfix声明后缀。
示例如下:
// 自定义接口方法
public interface UserDao {
User getUserById(Integer id);
}
//实现类
public class UserRepositoryImpl implements UserDao {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
public User getUserById(Integer id) {
User user = entityManager.find(User.class, id);
System.out.println("UserRepositoryImpl.test()");
return user;
}
}
//声明的通用接口
public interface UserRepository
extends UserDao,JpaRepository<User,Integer>,
JpaSpecificationExecutor<User> {
//...
}
//测试Controller
@GetMapping("/test16")
public User test16(Integer id){
User user = userRepository.getUserById(id);
return user;
}
查看控制台打印SQL如下:
SELECT
user0_.id AS id1_1_0_,
user0_.address_id AS address_5_1_0_,
user0_.add_id AS add_id2_1_0_,
user0_.email AS email3_1_0_,
user0_.last_name AS last_nam4_1_0_,
address1_.id AS id1_0_1_,
address1_.city AS city2_0_1_,
address1_.province AS province3_0_1_
FROM
tb_user user0_
LEFT OUTER JOIN tb_address address1_ ON user0_.address_id = address1_.id
WHERE
user0_.id =?
正常查询id为1的User对象并返回 !
关于SQL中连接查询与分类参考:MySQL中的连接分类详解
② 为所有的repository添加自定义方法
import java.io.Serializable;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.repository.NoRepositoryBean;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import com.jane.model.Address;
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface CommonMethodTest<T, ID extends Serializable> extends JpaRepository<T, ID>{
Address method();
}
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import com.jane.model.*;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.support.JpaEntityInformation;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.support.SimpleJpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.repository.NoRepositoryBean;
@NoRepositoryBean
public class CommonMethodTestImpl<T, ID extends Serializable>
extends SimpleJpaRepository<T, ID> implements CommonMethodTest<T, ID> {
private EntityManager entityManager;
public CommonMethodTestImpl(Class<T> domainClass, EntityManager em) {
super(domainClass, em);
}
public CommonMethodTestImpl(JpaEntityInformation<T, ?> entityInformation, EntityManager em) {
super(entityInformation, em);
this.entityManager = em;
}
@Override
public Address method() {
Address address = entityManager.find(Address.class, 1);
System.out.println("...BASE METHOD TEST...");
return address;
}
}
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.support.JpaMetamodelEntityInformation;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.support.JpaRepositoryFactory;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.support.JpaRepositoryFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.data.repository.Repository;
import org.springframework.data.repository.core.RepositoryMetadata;
import org.springframework.data.repository.core.support.RepositoryFactorySupport;
public class CommonJpaRepositoryFactoryBean<T extends Repository<S, ID>, S, ID extends Serializable>
extends JpaRepositoryFactoryBean<T, S, ID> {
public CommonJpaRepositoryFactoryBean(Class<? extends T> repositoryInterface) {
super(repositoryInterface);
}
protected RepositoryFactorySupport createRepositoryFactory(
EntityManager entityManager) {
return new CommonRepositoryFactory(entityManager);
}
private static class CommonRepositoryFactory<T, I extends Serializable>
extends JpaRepositoryFactory {
private EntityManager entityManager;
public CommonRepositoryFactory(EntityManager entityManager) {
super(entityManager);
this.entityManager = entityManager;
}
protected Object getTargetRepository(JpaMetamodelEntityInformation information) {
return new CommonMethodTestImpl<T, I>(information,entityManager);
}
// protected Object getTargetRepository(RepositoryMetadata metadata) {
//
// return new CommonMethodTestImpl<T, I>(
// (Class<T>) metadata.getDomainType(), entityManager);
// }
protected Class<?> getRepositoryBaseClass(RepositoryMetadata metadata) {
return CommonMethodTestImpl.class;
}
// protected Class<?> getRepositoryBaseClass(RepositoryMetadata metadata) {
// return CommonMethodTest.class;
// }
}
}
创建一个自定义的RepositoryFactoryBean来代替默认的RepositoryFactoryBean。
RepositoryFactoryBean负责返回一个RepositoryFactory,Spring Data Jpa 将使用RepositoryFactory来创建Repository具体实现。
这里我们用CommonMethodTestImpl代替SimpleJpaRepository作为Repository接口的实现。这样我们就能够达到为所有Repository添加自定义方法的目的。
public interface AddressRepository extends CommonMethodTest<Address, Integer>{
}
@SpringBootApplication
@EntityScan(basePackages={"com.jane.model"})
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = {"com.jane.dao"},repositoryFactoryBeanClass = CommonJpaRepositoryFactoryBean.class)
public class JpaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(JpaApplication.class, args);
}
}
我们需要配置Jpa使用我们自定义的CommonJpaRepositoryFactoryBean。
@RestController
public class AddressController {
@Autowired
AddressRepository addressRepository;
@GetMapping("/test17")
public Address test17(){
Address address = addressRepository.method();
return address;
}
}
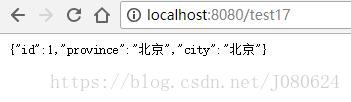
① 传统项目下如何处理
如下示例,JPA默认使用@ManyToOne(fetch=FetchType.EAGER)在获取User的时候会同时获取管理的Address:
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "address_id")
private Address address;
当然这会带来性能上的影响,可以使用如下方式开启懒加载:
@ManyToOne(fetch=FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "address_id")
private Address address;
此时返回结果中Address是为null,如果页面想要使用Address,将会抛出异常。
org.hibernate.LazyInitializationException:could not initialize proxy - no Session
(懒加载异常在默认情况下,hibernate为懒加载),这意味着在读取数据的时候,Session已经关闭。
这里推荐配置spring提供的OpenSessionInViewFilter的过滤器:
<filter>
<!-- 配置seeion作用时间不足而导页面需要查询数据session已经关闭问题,扩大作用时间 -->
<filter-name>OpenSessionInViewFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.support.OpenSessionInViewFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>OpenSessionInViewFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
在SpringDataJPA中更推荐使用OpenEntityManagerInViewFilter来替代OpenSessionInViewFilter:
<filter>
<filter-name>Spring OpenEntityManagerInViewFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.orm.jpa.support.OpenEntityManagerInViewFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<!-- 指定org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalEntityManagerFactoryBean在spring配置文件中的名称,默认值为entityManagerFactory
如果LocalEntityManagerFactoryBean在spring中的名称不是entityManagerFactory,该参数一定要指定,否则会出现找不到entityManagerFactory的例外 -->
<param-name>entityManagerFactoryBeanName</param-name>
<param-value>entityManagerFactory</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>Spring OpenEntityManagerInViewFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
② SpringBoot如何处理
SpringBoot做了一系列的自动配置,在项目启动后会自动进行初始化,如DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration、HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration等。
如果依赖中加入了其它功能的依赖,SpringBoot还会实现这些功能的自动适配,比如我们增加数据库的JPA的功能,就会启用对JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration的自动配置功能。
JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration如下:
/**
* {@link EnableAutoConfiguration Auto-configuration} for Spring Data's JPA Repositories.
* <p>
* Activates when there is a bean of type {@link javax.sql.DataSource} configured in the
* context, the Spring Data JPA
* {@link org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository} type is on the classpath,
* and there is no other, existing
* {@link org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository} configured.
* <p>
* Once in effect, the auto-configuration is the equivalent of enabling JPA repositories
* using the {@link org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories}
* annotation.
* <p>
* This configuration class will activate <em>after</em> the Hibernate auto-configuration.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Josh Long
* @see EnableJpaRepositories
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnBean(DataSource.class)
@ConditionalOnClass(JpaRepository.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({ JpaRepositoryFactoryBean.class,
JpaRepositoryConfigExtension.class })
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.data.jpa.repositories", name = "enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
@Import(JpaRepositoriesAutoConfigureRegistrar.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class)
public class JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration {
}
具体的可以自行跟踪该类上面的注解标签,即可明白。
application.properties配置:
spring.jpa.open-in-view=true //默认为true,可不配
该配置解释如下:
spring.jpa.open-in-view
java.lang.Boolean
Default: true
Register OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor.
Binds a JPA EntityManager to the thread for the entire processing
of the request.
该配置会注册一个OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor。在处理请求时,将 EntityManager 绑定到整个处理流程中(model->dao->service->controller),开启和关闭session。这样一来,就不会出现 no Session 的错误了(可以尝试将该配置的值置为 false, 就会出现懒加载的错误了。)
博文项目代码下载地址:GitHub项目地址
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!
