社区微信群开通啦,扫一扫抢先加入社区官方微信群

社区微信群
社区微信群开通啦,扫一扫抢先加入社区官方微信群

社区微信群
尊重原创,转载请标明出处 http://blog.csdn.net/abcdef314159
这里来分析一下Android自定义控件中比较常用的另一个类Path
/**
* The Path class encapsulates compound (multiple contour) geometric paths
* consisting of straight line segments, quadratic curves, and cubic curves.
* It can be drawn with canvas.drawPath(path, paint), either filled or stroked
* (based on the paint's Style), or it can be used for clipping or to draw
* text on a path.
*/ /**
* Specifies how closed shapes (e.g. rects, ovals) are oriented when they
* are added to a path.
*/
public enum Direction {
/** clockwise */
CW (1), // must match enum in SkPath.h
/** counter-clockwise */
CCW (2); // must match enum in SkPath.h
Direction(int ni) {
nativeInt = ni;
}
final int nativeInt;
}package test.view;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Paint.Style;
import android.graphics.Path;
import android.graphics.Path.Direction;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class PathView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
private Path mPath;
public PathView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mPaint.setStyle(Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(12);
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
mPath = new Path();
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
mPath.addRect(200, 100, 500, 300, Direction.CW);
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
mPath.reset();
mPath.addRect(200, 400, 500, 600, Direction.CCW);
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
}
}
两个图形基本一样,我们再来修改一下
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
mPath.addRect(200, 100, 500, 300, Direction.CW);
mPath.setLastPoint(50, 200);
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
mPath.reset();
mPath.addRect(200, 400, 500, 600, Direction.CW);
mPath.setLastPoint(50, 500);
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
mPath.addRect(200, 100, 500, 300, Direction.CW);
mPath.setLastPoint(50, 200);
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
mPath.reset();
mPath.addRect(200, 400, 500, 600, Direction.CCW);
mPath.setLastPoint(50, 500);
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
}两个完全不同,原因就在于一个是顺时针一个是逆时针,举个例子,比如说矩形的四个点按顺时针方向是ABCD,那么逆时针方向就是ADCB,所以在上面CW(顺时针)方向的时候setLastPoint的还是最后一个点D,所以没有变,当逆时针(CCW)方向的时候,最后一个点就变成了B,所以图形变了。下面在看一下当出现文字的时候就好理解了
package test.view;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Paint.Style;
import android.graphics.Path;
import android.graphics.RectF;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class PathView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
private Path mPath;
private RectF oval;
public PathView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mPaint.setStyle(Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(2);
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
mPaint.setTextSize(36);
mPath = new Path();
oval = new RectF(100, 100, 900, 600);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.translate(100, 100);
mPath.addOval(oval, Path.Direction.CW);
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
canvas.drawTextOnPath("123456789", mPath, 0, 0, mPaint);
mPath.reset();
mPath.addOval(oval, Path.Direction.CCW);
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
canvas.drawTextOnPath("123456789", mPath, 0, 0, mPaint);
}
}
下面的是顺时针方向的,上面的是逆时针方向的。OK,在继续看一下Path的其他方法,两个构造方法就不用说了,看一下reset()方法,清除线条,但没有改变他的填充类型,这里有4种类型,待会下面介绍,再看一下rewind()方法,清除线条但保持内部的数据结构,以便下次能快速使用。他俩的区别是reset保留填充类型,但没有保留原有数据结果,而rewind正好相反。在下面有一个枚举类Op
DIFFERENCE表示path1减去path2后剩下的部分
INTERSECT表示path1和path2公共的部分
UNION表示path1和path2都具有的部分
XOR表示path1和path2各自但不包含对方的部分
REVERSE_DIFFERENCE和DIFFERENCE差不多,不过他说path2减去path1后剩下的部分
直接上代码
package test.view;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Paint.Style;
import android.graphics.Path;
import android.graphics.Path.Direction;
import android.graphics.Path.Op;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class PathView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
private Path mPath1;
private Path mPath2;
public PathView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mPaint.setStyle(Style.FILL);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(20);
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
mPath1 = new Path();
mPath1.addCircle(300, 800, 280, Direction.CCW);
mPath2 = new Path();
mPath2.addRect(400, 900, 800, 1300, Direction.CCW);
mPath1.op(mPath2, Op.DIFFERENCE);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.drawPath(mPath1, mPaint);
}
}INTERSECT
UNION
XOR
REVERSE_DIFFERENCE
再看下一个枚举类FillType
WINDING表示取Path所有的区域
EVEN_ODD表示取path没有相交的区域
INVERSE_WINDING表示取path未占有的区域
INVERSE_EVEN_ODD表示取未占有和path相交的区域
其中WINDING和INVERSE_WINDING,EVEN_ODD和INVERSE_EVEN_ODD都是取的相反的。
老规矩,上代码
package test.view;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Paint.Style;
import android.graphics.Path;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class PathView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
private Path mPath;
public PathView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
mPaint.setStyle(Style.FILL_AND_STROKE);
mPath = new Path();
mPath.addCircle(300, 300, 200, Path.Direction.CW);
mPath.addCircle(600, 300, 200, Path.Direction.CW);
mPath.setFillType(Path.FillType.WINDING);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
}
}
EVEN_ODD
INVERSE_WINDING
INVERSE_EVEN_ODD
下面再来看一下path的其他的一些方法,setFillType(FillType ft)表示设置填充类型。isInverseFillType()表示填充类型是否是相反的,也就是INVERSE_WINDING或者INVERSE_EVEN_ODD。toggleInverseFillType()表示置为相反的状态。isEmpty()表示Path路线是否是空的。isRect(RectF rect)表示路径是否是指定的矩形。computeBounds(RectF bounds, boolean exact)计算路径的边界保存到bounds中,exact参数没用,如果只有0或1个点,则bounds为(0,0,0,0),否则提取到他的边界保存到bounds中,看一下代码
mPath.addCircle(300, 300, 200, Path.Direction.CW);
RectF mRectF = new RectF();
mPath.computeBounds(mRectF, true);
Log.d("wld__________", mRectF.left + "," + mRectF.top + ","
+ mRectF.right + "," + mRectF.bottom);
incReserve(int extraPtCount)表示将path增加extraPtCount个点,这能使path有效率的分配它的存储空间;
moveTo(float x, float y)移动到坐标为(x,y)的位置
rMoveTo(float dx, float dy)这个是相对位置,相对上一个位置的增量,如果上一个轮廓没有,则相当于moveTo()方法
lineTo(float x, float y)增加一条从上一个点到这一个点的线,如果moveTo()方法没有调用,则上一个点坐标为(0,0),
rLineTo(float dx, float dy)和lineTo(float dx, float dy)类似,只不过他是增量。
quadTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2)和rQuadTo(float dx1, float dy1, float dx2, float dy2)表示增加一个二次方的贝赛尔曲线,看一下代码
package test.view;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Paint.Style;
import android.graphics.Path;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
public class PathView extends View {
private Paint mPaint;
private Path mPath;
public PathView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
mPaint.setStyle(Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(8);
mPath = new Path();
mPath.moveTo(200, 200);
mPath.lineTo(500, 500);
mPath.lineTo(800, 200);
mPath.moveTo(200, 200);
mPath.quadTo(500, 500, 800, 200);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
}
}cubicTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2,float x3, float y3)和rCubicTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2,float x3, float y3)表示三次贝赛尔曲线,看一下代码
mPath.moveTo(200, 200);
mPath.lineTo(500, 500);
mPath.lineTo(800, 200);
mPath.lineTo(1000, 500);
mPath.moveTo(200, 200);
mPath.cubicTo(500, 500, 800, 200, 1000, 500);运行结果如下

arcTo有三个重载的方法,下面只看其中的一个arcTo(float left, float top, float right, float bottom, float startAngle,float sweepAngle, boolean forceMoveTo)
增加一段指定的弧形连接到path当中,作为一个新的轮廓,如果path的最后一个点和弧形的第一个点不一样,那么就会先通过lineTo()将这两个点连接起来,然后再连接圆弧。如果path是空的,那就会调用moveTo()把path的第一个点移到圆弧的第一个点上来,其中startAngle是开始角度,其中水平往右为0度,sweepAngle是圆弧扫过的角度,按顺时针方向扫描,forceMoveTo表示是否和上一个轮廓连接,如果为false表示连接,如果为true表示不连接,看一下代码
mPath.moveTo(100, 100);
mPath.lineTo(400, 400);
mPath.lineTo(600, 200);
mPath.arcTo(700, 300, 900, 700, 0, 135, false);
在修改一下
mPath.arcTo(700, 300, 900, 700, 0, 135, true);没有连接,如果sweepAngle大于360度的时候,会用sweepAngle对360求余,结果就不在演示了。
close()是关闭当前轮廓,如果起始点和终止点不重叠就会用一条直线连接。
addRect(RectF rect, Direction dir)和addRect(float left, float top, float right, float bottom, Direction dir)增加一个闭合的矩形到path当中,看代码
mPath.moveTo(100, 100);
mPath.lineTo(400, 400);
mPath.lineTo(600, 200);
mPath.addRect(700, 300, 900, 700, Direction.CCW);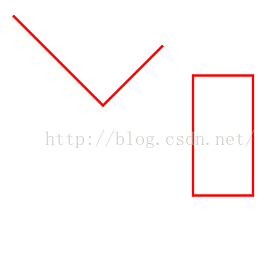
mPath.moveTo(100, 100);
mPath.lineTo(400, 400);
mPath.lineTo(600, 200);
mPath.addOval(700, 300, 900, 700, Direction.CCW);
addCircle(float x, float y, float radius, Direction dir)增加一个圆形轮廓到path中,
addArc(RectF oval, float startAngle, float sweepAngle)和addArc(float left, float top, float right, float bottom, float startAngle, float sweepAngle)添加一个指定的弧形到path中作为一个新的轮廓,如果arcTo方法中的最后一个参数为true,和这个方法基本上一样。
addRoundRect增加圆角矩形,看代码
mPath.moveTo(100, 100);
mPath.lineTo(400, 400);
mPath.lineTo(600, 200);
mPath.addRoundRect(700, 300, 900, 700, 50, 50, Direction.CCW);
再来修改一下
mPath.addRoundRect(700, 300, 900, 700, 50, 100, Direction.CCW); mPath.addRoundRect(700, 300, 900, 700, new float[] { 20, 20, 40, 40,
80, 80, 20, 100 }, Direction.CCW);addPath(Path src, float dx, float dy),addPath(Path src)和addPath(Path src, Matrix matrix)表示将src添加到path中,dx,dy是偏移量,matrix是转换的矩阵,看代码
Matrix mMatrix = new Matrix();
mPath = new Path();
mPath.moveTo(100, 100);
mPath.lineTo(400, 400);
mPath.lineTo(600, 200);
mPath1 = new Path();
mPath1.moveTo(100, 500);
mPath1.lineTo(400, 800);
mPath1.lineTo(600, 600);
mMatrix.postTranslate(300, 0);
mPath.addPath(mPath1, mMatrix);offset(float dx, float dy)表示将path平移dx,dy
offset(float dx, float dy, Path dst)表示将当前path平移(dx,dy)之后存储到dst中。
setLastPoint(float dx, float dy)设置轮廓的最后一个点。
transform(Matrix matrix, Path dst)将path进行matrix变化后,将结果保存到dst当中,如果dst=null,将结果保存到当前path当中
transform(Matrix matrix)对当前path进行matrix变换。
OK,目前为止Path的方法已经分析完毕。
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!
