社区微信群开通啦,扫一扫抢先加入社区官方微信群

社区微信群
社区微信群开通啦,扫一扫抢先加入社区官方微信群

社区微信群
java的数组与Arrays类源码详解
java.util.Arrays 类是 JDK 提供的一个工具类,用来处理数组的各种方法,而且每个方法基本上都是静态方法,能直接通过类名Arrays调用。
类的定义
public final
class Array {
private Array() {}
public static Object newInstance(Class<?> componentType, int length)
throws NegativeArraySizeException {
return newArray(componentType, length);
}
public static Object newInstance(Class<?> componentType, int... dimensions)
throws IllegalArgumentException, NegativeArraySizeException {
return multiNewArray(componentType, dimensions);
}
public static native int getLength(Object array)
throws IllegalArgumentException;
public static native Object get(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native boolean getBoolean(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native byte getByte(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native char getChar(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native short getShort(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native int getInt(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native long getLong(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native float getFloat(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native double getDouble(Object array, int index)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void set(Object array, int index, Object value)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setBoolean(Object array, int index, boolean z)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setByte(Object array, int index, byte b)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setChar(Object array, int index, char c)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setShort(Object array, int index, short s)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setInt(Object array, int index, int i)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setLong(Object array, int index, long l)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setFloat(Object array, int index, float f)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
public static native void setDouble(Object array, int index, double d)
throws IllegalArgumentException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException;
private static native Object newArray(Class<?> componentType, int length)
throws NegativeArraySizeException;
private static native Object multiNewArray(Class<?> componentType,
int[] dimensions)
throws IllegalArgumentException, NegativeArraySizeException;
}java.lang.reflect.Array.setChar(Object array, int index, double value)方法将指定数组对象的索引组件的值设置为指定的double值。
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] array = new double[]{1.0,2.0,3.0};
Array.setDouble(array, 0, 2.0);
Array.setDouble(array, 1, 3.0);
Array.setDouble(array, 2, 4.0);
System.out.println("array[0] = " + Array.getDouble(array, 0));
System.out.println("array[1] = " + Array.getDouble(array, 1));
System.out.println("array[2] = " + Array.getDouble(array, 2));
}
}编译并运行上面的程序,将产生以下结果 -
array[0] = 2.0
array[1] = 3.0
array[2] = 4.0Arrays类的定义
public class Arrays {
private static final int MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN = 1 << 13;
// Suppresses default constructor, ensuring non-instantiability.
private Arrays() {}
static final class NaturalOrder implements Comparator<Object> {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public int compare(Object first, Object second) {
return ((Comparable<Object>)first).compareTo(second);
}
static final NaturalOrder INSTANCE = new NaturalOrder();
}
private static void rangeCheck(int arrayLength, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex > toIndex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"fromIndex(" + fromIndex + ") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
}
if (fromIndex < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(fromIndex);
}
if (toIndex > arrayLength) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(toIndex);
}
}
public static void sort(int[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(long[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(short[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(char[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(byte[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
public static void sort(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1);
}
public static void sort(float[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(double[] a) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void sort(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
}
public static void parallelSort(byte[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJByte.Sorter
(null, a, new byte[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJByte.Sorter
(null, a, new byte[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(char[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJChar.Sorter
(null, a, new char[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJChar.Sorter
(null, a, new char[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(short[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJShort.Sorter
(null, a, new short[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJShort.Sorter
(null, a, new short[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(int[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJInt.Sorter
(null, a, new int[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJInt.Sorter
(null, a, new int[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(long[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJLong.Sorter
(null, a, new long[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJLong.Sorter
(null, a, new long[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(float[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJFloat.Sorter
(null, a, new float[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJFloat.Sorter
(null, a, new float[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(double[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, n - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJDouble.Sorter
(null, a, new double[n], 0, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
public static void parallelSort(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJDouble.Sorter
(null, a, new double[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void parallelSort(T[] a) {
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
TimSort.sort(a, 0, n, NaturalOrder.INSTANCE, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJObject.Sorter<T>
(null, a,
(T[])Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), n),
0, n, 0, ((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g, NaturalOrder.INSTANCE).invoke();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>>
void parallelSort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
TimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, NaturalOrder.INSTANCE, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJObject.Sorter<T>
(null, a,
(T[])Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), n),
fromIndex, n, 0, ((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g, NaturalOrder.INSTANCE).invoke();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> void parallelSort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> cmp) {
if (cmp == null)
cmp = NaturalOrder.INSTANCE;
int n = a.length, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
TimSort.sort(a, 0, n, cmp, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJObject.Sorter<T>
(null, a,
(T[])Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), n),
0, n, 0, ((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g, cmp).invoke();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> void parallelSort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Comparator<? super T> cmp) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (cmp == null)
cmp = NaturalOrder.INSTANCE;
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN ||
(p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1)
TimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, cmp, null, 0, 0);
else
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJObject.Sorter<T>
(null, a,
(T[])Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), n),
fromIndex, n, 0, ((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g, cmp).invoke();
}
static final class LegacyMergeSort {
private static final boolean userRequested =
java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
new sun.security.action.GetBooleanAction(
"java.util.Arrays.useLegacyMergeSort")).booleanValue();
}
public static void sort(Object[] a) {
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a);
else
ComparableTimSort.sort(a, 0, a.length, null, 0, 0);
}
/** To be removed in a future release. */
private static void legacyMergeSort(Object[] a) {
Object[] aux = a.clone();
mergeSort(aux, a, 0, a.length, 0);
}
public static void sort(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
else
ComparableTimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, null, 0, 0);
}
/** To be removed in a future release. */
private static void legacyMergeSort(Object[] a,
int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
Object[] aux = copyOfRange(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
mergeSort(aux, a, fromIndex, toIndex, -fromIndex);
}
private static final int INSERTIONSORT_THRESHOLD = 7;
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
private static void mergeSort(Object[] src,
Object[] dest,
int low,
int high,
int off) {
int length = high - low;
// Insertion sort on smallest arrays
if (length < INSERTIONSORT_THRESHOLD) {
for (int i=low; i<high; i++)
for (int j=i; j>low &&
((Comparable) dest[j-1]).compareTo(dest[j])>0; j--)
swap(dest, j, j-1);
return;
}
// Recursively sort halves of dest into src
int destLow = low;
int destHigh = high;
low += off;
high += off;
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
mergeSort(dest, src, low, mid, -off);
mergeSort(dest, src, mid, high, -off);
// If list is already sorted, just copy from src to dest. This is an
// optimization that results in faster sorts for nearly ordered lists.
if (((Comparable)src[mid-1]).compareTo(src[mid]) <= 0) {
System.arraycopy(src, low, dest, destLow, length);
return;
}
// Merge sorted halves (now in src) into dest
for(int i = destLow, p = low, q = mid; i < destHigh; i++) {
if (q >= high || p < mid && ((Comparable)src[p]).compareTo(src[q])<=0)
dest[i] = src[p++];
else
dest[i] = src[q++];
}
}
private static void swap(Object[] x, int a, int b) {
Object t = x[a];
x[a] = x[b];
x[b] = t;
}
public static <T> void sort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> c) {
if (c == null) {
sort(a);
} else {
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a, c);
else
TimSort.sort(a, 0, a.length, c, null, 0, 0);
}
}
/** To be removed in a future release. */
private static <T> void legacyMergeSort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> c) {
T[] aux = a.clone();
if (c==null)
mergeSort(aux, a, 0, a.length, 0);
else
mergeSort(aux, a, 0, a.length, 0, c);
}
public static <T> void sort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Comparator<? super T> c) {
if (c == null) {
sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
} else {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, c);
else
TimSort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex, c, null, 0, 0);
}
}
/** To be removed in a future release. */
private static <T> void legacyMergeSort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Comparator<? super T> c) {
T[] aux = copyOfRange(a, fromIndex, toIndex);
if (c==null)
mergeSort(aux, a, fromIndex, toIndex, -fromIndex);
else
mergeSort(aux, a, fromIndex, toIndex, -fromIndex, c);
}
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
private static void mergeSort(Object[] src,
Object[] dest,
int low, int high, int off,
Comparator c) {
int length = high - low;
// Insertion sort on smallest arrays
if (length < INSERTIONSORT_THRESHOLD) {
for (int i=low; i<high; i++)
for (int j=i; j>low && c.compare(dest[j-1], dest[j])>0; j--)
swap(dest, j, j-1);
return;
}
// Recursively sort halves of dest into src
int destLow = low;
int destHigh = high;
low += off;
high += off;
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
mergeSort(dest, src, low, mid, -off, c);
mergeSort(dest, src, mid, high, -off, c);
// If list is already sorted, just copy from src to dest. This is an
// optimization that results in faster sorts for nearly ordered lists.
if (c.compare(src[mid-1], src[mid]) <= 0) {
System.arraycopy(src, low, dest, destLow, length);
return;
}
// Merge sorted halves (now in src) into dest
for(int i = destLow, p = low, q = mid; i < destHigh; i++) {
if (q >= high || p < mid && c.compare(src[p], src[q]) <= 0)
dest[i] = src[p++];
else
dest[i] = src[q++];
}
}该方法是用于数组排序,在 Arrays 类中有该方法的一系列重载方法,能对7种基本数据类型,包括 byte,char,double,float,int,long,short 等都能进行排序,还有 Object 类型(实现了Comparable接口),以及比较器 Comparator

Arrays类中的sort()使用的是经过调优的快速排序算法;
对于int[],double[],char[]等基本数据类型的数组,Arrays类只提供了默认的升序排列,并没有提供相应的降序排列方法;
数组排序函数原型:
static void sort(int[] a) 对指定的int型数组按数字升序进行排序
static void sort (int[] a,int fromIndex,int toIndex) 对指定int型数组的指定范围按数字升序进行排序
快速排序的思想是:首先选取一个基准,这个基准可以是第一个数字也可以是任意数值,然后用两个指针left和right分别指向所要排序的数组的0号位置和length-1号位置,在保证left<right的前提下,先从后向前遍历寻找第一个小于该基准的数字,进而与left位置的数字进行交换,接下来再从前向后遍历寻找第一个大于该基准的数字,进而与right所指向的位置的数字进行交换,以此类推,一次遍历下来我们将会的到一个在基准左边都是小于基准的数字,在基准右边都是大于基准的数字。快速排序在一般情况下它的时间复杂度为O(n*logn),但是在我们输入一组完全有序或者基本有序的数组的情况下,快速排序算法将退换为冒泡排序算法,时间复杂度会变味O(n^2),这种情况也是可以改变的,当我们在选取基准时,我们可以采用三位取中法,即在arr[left],arr[(left+right)/2],arr[right]三者中取中间值作为基准,这样会避免我们在最坏情况下快速排序算法性能的降低。
①、基本类型的数组
这里我们以 int[ ] 为例看看:
int[] num = {1,3,8,5,2,4,6,7};
Arrays.sort(num);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num));//[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]通过调用 sort(int[] a) 方法,将原数组按照升序的顺序排列。
在 Arrays.sort 方法内部调用 DualPivotQuicksort.sort 方法,这个方法的源码很长,分别对于数组的长度进行了各种算法的划分,包括快速排序,插入排序,冒泡排序都有使用。
②、对象类型数组
该类型的数组进行排序可以实现 Comparable 接口,重写 compareTo 方法进行排序。
String[] str = {"a","f","c","d"};
Arrays.sort(str);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str));//[a, c, d, f]String 类型实现了 Comparable 接口,内部的 compareTo 方法是按照字典码进行比较的。
③、没有实现Comparable接口的,可以通过Comparator实现排序
Person[] p = new Person[]{new Person("zhangsan",22),new Person("wangwu",11),new Person("lisi",33)};
Arrays.sort(p,new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
if(o1 == null || o2 == null){
return 0;
}
return o1.getPage()-o2.getPage();
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(p));④、进行降序排序,可以这么做
Arrays.sort(a,Collections.reverseOrder()); 但是要注意的是,不能使用基本类型(int,double, char),如果是int型需要改成Integer,float要改成Float,例如;
Integer[] a = new Integer[10];
Float[] a = new Float[10];
//上面的例子可以改成
Integer[] a = {9, 8, 7, 2, 3, 4, 1, 0, 6, 5}; comparetor可以用于sort方法对数组直接进行降序排序
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class ArraysDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int包装类对象数组,赋值
Integer[] arr = {12,15,32,16,20,25};
//传入引用类型对象arr,用匿名类实现Comparator接口,i1在前则为升序,反正降序
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer i1, Integer i2) {
int num = i2 - i1;
return num;
}
});
//打印数组
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
既然这里用到了Comparator比较器对象,那我们就来说说Java中的两种比较器Comparable和Comparator
区别:①Comparable位于java.lang包下,Comparator位于java.util包下;
②实现Comparable接口要重写ComparetTo()方法,实现Comparator接口需要重写compare()方法;
③Comparable接口将比较代码嵌入需要进行比较的类的自身代码中,Comparator接口要在一个单独的类中实现比较;
④如果前期类设计没有考虑到类的比较问题而没有实现Comparable接口,后期可以通过Comparator接口来实现算法进行排序;
⑤Comparable接口强制进行自然排序,Comparator接口不强制自然排序,可以指定排序
public static int binarySearch(long[] a, long key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
long key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
long key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
long midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
int key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
int key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
int midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(short[] a, short key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
short key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
short key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
short midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(char[] a, char key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
char key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
char key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
char midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(byte[] a, byte key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
byte key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
byte key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
byte midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(double[] a, double key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
double key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
double key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
double midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1; // Neither val is NaN, thisVal is smaller
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1; // Neither val is NaN, thisVal is larger
else {
long midBits = Double.doubleToLongBits(midVal);
long keyBits = Double.doubleToLongBits(key);
if (midBits == keyBits) // Values are equal
return mid; // Key found
else if (midBits < keyBits) // (-0.0, 0.0) or (!NaN, NaN)
low = mid + 1;
else // (0.0, -0.0) or (NaN, !NaN)
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(float[] a, float key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
float key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
float key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
float midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1; // Neither val is NaN, thisVal is smaller
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1; // Neither val is NaN, thisVal is larger
else {
int midBits = Float.floatToIntBits(midVal);
int keyBits = Float.floatToIntBits(key);
if (midBits == keyBits) // Values are equal
return mid; // Key found
else if (midBits < keyBits) // (-0.0, 0.0) or (!NaN, NaN)
low = mid + 1;
else // (0.0, -0.0) or (NaN, !NaN)
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static int binarySearch(Object[] a, Object key) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key);
}
public static int binarySearch(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Object key) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static int binarySearch0(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
Object key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Comparable midVal = (Comparable)a[mid];
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
int cmp = midVal.compareTo(key);
if (cmp < 0)
low = mid + 1;
else if (cmp > 0)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
public static <T> int binarySearch(T[] a, T key, Comparator<? super T> c) {
return binarySearch0(a, 0, a.length, key, c);
}
public static <T> int binarySearch(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
T key, Comparator<? super T> c) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key, c);
}
// Like public version, but without range checks.
private static <T> int binarySearch0(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
T key, Comparator<? super T> c) {
if (c == null) {
return binarySearch0(a, fromIndex, toIndex, key);
}
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
T midVal = a[mid];
int cmp = c.compare(midVal, key);
if (cmp < 0)
low = mid + 1;
else if (cmp > 0)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
用二分法查找数组中的某个元素。该方法和 sort 方法一样,适用于各种基本数据类型以及对象。
注意:二分法是对以及有序的数组进行查找(比如先用Arrays.sort()进行排序,然后调用此方法进行查找)。找到元素返回下标,没有则返回 -1
实例:
int[] num = {1,3,8,5,2,4,6,7};
Arrays.sort(num);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num));//[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(num, 2));//返回元素的下标 1 public static boolean equals(long[] a, long[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(int[] a, int[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(short[] a, short a2[]) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(char[] a, char[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(byte[] a, byte[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(boolean[] a, boolean[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (a[i] != a2[i])
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(double[] a, double[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (Double.doubleToLongBits(a[i])!=Double.doubleToLongBits(a2[i]))
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(float[] a, float[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++)
if (Float.floatToIntBits(a[i])!=Float.floatToIntBits(a2[i]))
return false;
return true;
}
public static boolean equals(Object[] a, Object[] a2) {
if (a==a2)
return true;
if (a==null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i=0; i<length; i++) {
Object o1 = a[i];
Object o2 = a2[i];
if (!(o1==null ? o2==null : o1.equals(o2)))
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static boolean deepEquals(Object[] a1, Object[] a2) {
if (a1 == a2)
return true;
if (a1 == null || a2==null)
return false;
int length = a1.length;
if (a2.length != length)
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Object e1 = a1[i];
Object e2 = a2[i];
if (e1 == e2)
continue;
if (e1 == null)
return false;
// Figure out whether the two elements are equal
boolean eq = deepEquals0(e1, e2);
if (!eq)
return false;
}
return true;
}
static boolean deepEquals0(Object e1, Object e2) {
assert e1 != null;
boolean eq;
if (e1 instanceof Object[] && e2 instanceof Object[])
eq = deepEquals ((Object[]) e1, (Object[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof byte[] && e2 instanceof byte[])
eq = equals((byte[]) e1, (byte[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof short[] && e2 instanceof short[])
eq = equals((short[]) e1, (short[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof int[] && e2 instanceof int[])
eq = equals((int[]) e1, (int[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof long[] && e2 instanceof long[])
eq = equals((long[]) e1, (long[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof char[] && e2 instanceof char[])
eq = equals((char[]) e1, (char[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof float[] && e2 instanceof float[])
eq = equals((float[]) e1, (float[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof double[] && e2 instanceof double[])
eq = equals((double[]) e1, (double[]) e2);
else if (e1 instanceof boolean[] && e2 instanceof boolean[])
eq = equals((boolean[]) e1, (boolean[]) e2);
else
eq = e1.equals(e2);
return eq;
}①、equals
equals 用来比较两个数组中对应位置的每个元素是否相等。

②、deepEquals
也是用来比较两个数组的元素是否相等,不过 deepEquals 能够进行比较多维数组,而且是任意层次的嵌套数组。
String[][] name1 = {{ "G","a","o" },{ "H","u","a","n"},{ "j","i","e"}};
String[][] name2 = {{ "G","a","o" },{ "H","u","a","n"},{ "j","i","e"}};
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(name1,name2));// false
System.out.println(Arrays.deepEquals(name1,name2));// true public static void fill(long[] a, long val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, long val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(int[] a, int val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, int val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(short[] a, short val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(short[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, short val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(char[] a, char val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(char[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, char val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(byte[] a, byte val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(byte[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, byte val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(boolean[] a, boolean val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(boolean[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
boolean val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(double[] a, double val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(double[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,double val){
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(float[] a, float val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(float[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, float val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(Object[] a, Object val) {
for (int i = 0, len = a.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
public static void fill(Object[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, Object val) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++)
a[i] = val;
}
// Cloning
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) {
return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass());
}
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static byte[] copyOf(byte[] original, int newLength) {
byte[] copy = new byte[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static short[] copyOf(short[] original, int newLength) {
short[] copy = new short[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static int[] copyOf(int[] original, int newLength) {
int[] copy = new int[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static long[] copyOf(long[] original, int newLength) {
long[] copy = new long[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static char[] copyOf(char[] original, int newLength) {
char[] copy = new char[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static float[] copyOf(float[] original, int newLength) {
float[] copy = new float[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static double[] copyOf(double[] original, int newLength) {
double[] copy = new double[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static boolean[] copyOf(boolean[] original, int newLength) {
boolean[] copy = new boolean[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T[] copyOfRange(T[] original, int from, int to) {
return copyOfRange(original, from, to, (Class<? extends T[]>) original.getClass());
}
public static <T,U> T[] copyOfRange(U[] original, int from, int to, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static byte[] copyOfRange(byte[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
byte[] copy = new byte[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static short[] copyOfRange(short[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
short[] copy = new short[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static int[] copyOfRange(int[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
int[] copy = new int[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static long[] copyOfRange(long[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
long[] copy = new long[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static char[] copyOfRange(char[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
char[] copy = new char[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static float[] copyOfRange(float[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
float[] copy = new float[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static double[] copyOfRange(double[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
double[] copy = new double[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static boolean[] copyOfRange(boolean[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
boolean[] copy = new boolean[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}fill
该系列方法用于给数组赋值,并能指定某个范围赋值。
copyOf
拷贝数组元素。底层采用 System.arraycopy() 实现,这是一个native方法。
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);src:源数组
srcPos:源数组要复制的起始位置
dest:目的数组
destPos:目的数组放置的起始位置
length:复制的长度
注意:src 和 dest都必须是同类型或者可以进行转换类型的数组。
int[] num1 = {1,2,3};
int[] num2 = new int[3];
System.arraycopy(num1, 0, num2, 0, num1.length);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(num2));//[1, 2, 3] @SafeVarargs
@SuppressWarnings("varargs")
public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a) {
return new ArrayList<>(a);
}
/**
* @serial include
*/
private static class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements RandomAccess, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2764017481108945198L;
private final E[] a;
ArrayList(E[] array) {
a = Objects.requireNonNull(array);
}
@Override
public int size() {
return a.length;
}
@Override
public Object[] toArray() {
return a.clone();
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
int size = size();
if (a.length < size)
return Arrays.copyOf(this.a, size,
(Class<? extends T[]>) a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(this.a, 0, a, 0, size);
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
@Override
public E get(int index) {
return a[index];
}
@Override
public E set(int index, E element) {
E oldValue = a[index];
a[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
@Override
public int indexOf(Object o) {
E[] a = this.a;
if (o == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
if (a[i] == null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
if (o.equals(a[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(a, Spliterator.ORDERED);
}
@Override
public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for (E e : a) {
action.accept(e);
}
}
@Override
public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
E[] a = this.a;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i] = operator.apply(a[i]);
}
}
@Override
public void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
Arrays.sort(a, c);
}
}作用是返回由指定数组支持的固定大小列表。
注意:这个方法返回的 ArrayList 不是我们常用的集合类 java.util.ArrayList。这里的 ArrayList 是 Arrays 的一个内部类 java.util.Arrays.ArrayList。这个内部类有如下属性和方法:
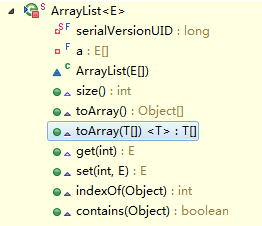
①、返回的 ArrayList 数组是一个定长列表,我们只能对其进行查看或者修改,但是不能进行添加或者删除操作
通过源码我们发现该类是没有add()或者remove() 这样的方法的,如果对其进行增加或者删除操作,都会调用其父类 AbstractList 对应的方法,而追溯父类的方法最终会抛出 UnsupportedOperationException 异常。如下:
String[] str = {"a","b","c"};
List<String> listStr = Arrays.asList(str);
listStr.set(1, "e");//可以进行修改
System.out.println(listStr.toString());//[a, e, c]
listStr.add("a");//添加元素会报错 java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException 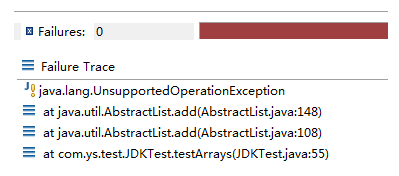
②、引用类型的数组和基本类型的数组区别
String[] str = {"a","b","c"};
List listStr = Arrays.asList(str);
System.out.println(listStr.size());//3
int[] i = {1,2,3};
List listI = Arrays.asList(i);
System.out.println(listI.size());//1上面的结果第一个listStr.size()==3,而第二个 listI.size()==1。这是为什么呢?
我们看源码,在 Arrays.asList 中,方法声明为 <T> List<T> asList(T... a)。该方法接收一个可变参数,并且这个可变参数类型是作为泛型的参数。我们知道基本数据类型是不能作为泛型的参数的,但是数组是引用类型,所以数组是可以泛型化的,于是 int[] 作为了整个参数类型,而不是 int 作为参数类型。
所以将上面的方法泛型化补全应该是:
String[] str = {"a","b","c"};
List<String> listStr = Arrays.asList(str);
System.out.println(listStr.size());//3
int[] i = {1,2,3};
List<int[]> listI = Arrays.asList(i);//注意这里List参数为 int[] ,而不是 int
System.out.println(listI.size());//1
Integer[] in = {1,2,3};
List<Integer> listIn = Arrays.asList(in);//这里参数为int的包装类Integer,所以集合长度为3
System.out.println(listIn.size());//3③、返回的列表ArrayList里面的元素都是引用,不是独立出来的对象
String[] str = {"a","b","c"};
List<String> listStr = Arrays.asList(str);
//执行更新操作前
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str));//[a, b, c]
listStr.set(0, "d");//将第一个元素a改为d
//执行更新操作后
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(str));//[d, b, c]我们看修改集合的内容,原数组的内容也变化了,所以这里传入的是引用类型。
④、已知数组数据,如何快速获取一个可进行增删改查的列表List?
String[] str = {"a","b","c"};
List<String> listStr = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(str));
listStr.add("d");
System.out.println(listStr.size());//4这里的ArrayList 集合类后面我们会详细讲解,大家目前只需要知道有这种用法即可。
⑤、Arrays.asList() 方法使用场景
Arrays工具类提供了一个方法asList, 使用该方法可以将一个变长参数或者数组转换成List 。但是,生成的List的长度是固定的;能够进行修改操作(比如,修改某个位置的元素);不能执行影响长度的操作(如add、remove等操作
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!
