社区微信群开通啦,扫一扫抢先加入社区官方微信群

社区微信群
社区微信群开通啦,扫一扫抢先加入社区官方微信群

社区微信群
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor继承自ThreadPoolExecutor,它主要用来在给定的延迟后运行任务,或者定期执行任务,类似Timer,但是其更强大更灵活,可以在构造函数指定多个对应的后台线程数
/**
* 实现ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
* @return
*/
public ExecutorService scheduledThreadPoolExecutor(){
return Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(8);
}
ScheduledExecutorService接口定义了可以选择执行的延时任务类型
//可调度的执行者服务接口
public interface ScheduledExecutorService extends ExecutorService {
//指定时延后调度执行任务
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command,
long delay, TimeUnit unit);
//指定时延后调度执行任务
public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable,
long delay, TimeUnit unit);
//指定时延后开始执行任务,以后每隔period的时长再次执行该任务
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit);
//指定时延后开始执行任务,以后任务执行完成后等待delay时长,再次执行任务
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit);
}
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit) {
//传参判空
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//直接返回第二个参数new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command, null,triggerTime(delay, unit)))获得ScheduledFutureTask对象
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> t = decorateTask(command,
new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command, null,
triggerTime(delay, unit)));
//执行延迟任务
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
}
protected <V> RunnableScheduledFuture<V> decorateTask(
Runnable runnable, RunnableScheduledFuture<V> task) {
return task;
}
//ScheduledFutureTask类是ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的内部类
ScheduledFutureTask(Runnable r, V result, long ns, long period) {
//调用父类FutureTask的构造方法
super(r, result);
//time表示任务下次执行的时间
this.time = ns;
//周期任务,正数表示按照固定速率,负数表示按照固定时延
this.period = period;
//任务的编号,通过线程池的sequencer成员变量从0开始生成编号。
this.sequenceNumber = sequencer.getAndIncrement();
}
/**
*执行延迟任务
*/
private void delayedExecute(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> task) {
//线程池已经关闭,调用拒绝执行处理器处理
if (isShutdown())
reject(task);
else {
//将任务加入到等待队列
super.getQueue().add(task);
//线程池已经关闭,且当前状态不能运行该任务,将该任务从等待队列移除并取消该任务
if (isShutdown() &&
!canRunInCurrentRunState(task.isPeriodic()) &&
remove(task))
task.cancel(false);
else
//增加一个worker,就算corePoolSize=0也要增加一个worker
ensurePrestart();
}
}
如果提交的是callable任务,可以通过返回的对象t.get()获取返回值
DelayQueue封装了一个优先队列
public class DelayQueue<E extends Delayed> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E> {
private final transient ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private final PriorityQueue<E> q = new PriorityQueue<E>();
.....
}
这个队列会对队列中的任务进行排序,timer小的排前面先被执行,如果两个timer相同,则比较sequenceNumber,该number小的先被执行(先提交的先执行)
执行流程:
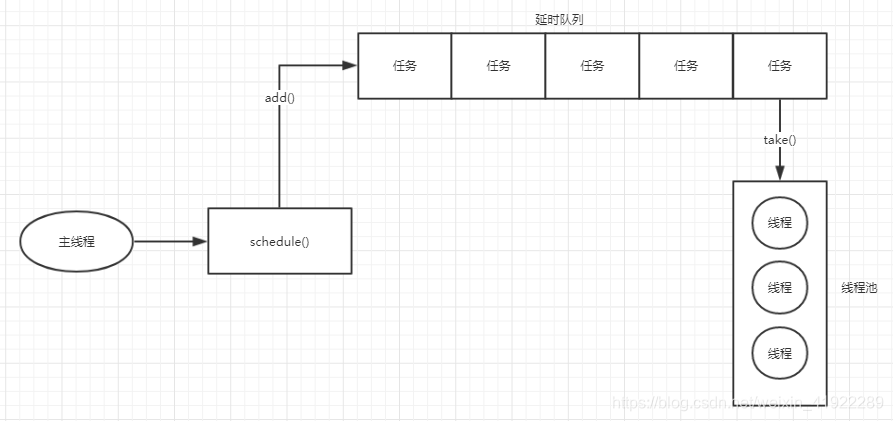
scheduleAtFixedRate:该方法在initialDelay时长后第一次执行任务,以后每隔period时长,再次执行任务。注意,period是从任务开始执行算起的。开始执行任务后,定时器每隔period时长检查该任务是否完成,如果完成则再次启动任务,否则等该任务结束后才再次启动任务,看下图示例。
//注意,固定速率和固定时延,传入的参数都是Runnable,也就是说这种定时任务是没有返回值的
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (period <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
//创建一个有初始延时和固定周期的任务
ScheduledFutureTask<Void> sft =
new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command,
null,
triggerTime(initialDelay, unit),
unit.toNanos(period));
RunnableScheduledFuture<Void> t = decorateTask(command, sft);
//outerTask表示将会重新入队的任务
sft.outerTask = t;
//稍后说明
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
}
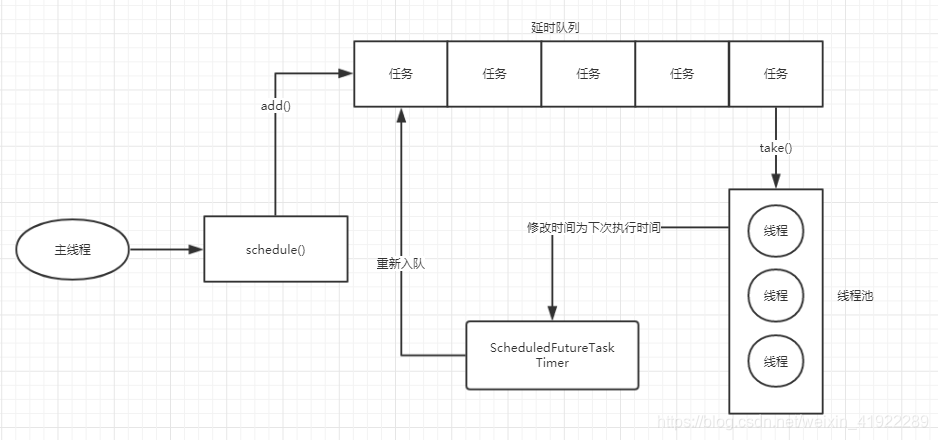
scheduleWithFixDelay:该方法在initialDelay时长后第一次执行任务,以后每当任务执行完成后,等待delay时长,再次执行任务,看下图示例。
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (delay <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
ScheduledFutureTask<Void> sft =
new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command,
null,
triggerTime(initialDelay, unit),
unit.toNanos(-delay));
RunnableScheduledFuture<Void> t = decorateTask(command, sft);
sft.outerTask = t;
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
}
执行流程:
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!
