几何信息和拓扑关系是地理信息系统中描述地理要素的空间位置和空间关系的不可缺少的基本信息。其中几何信息主要涉及几何目标的坐标位置、方向、角度、距离和面积等信息,它通常用解析几何的方法来分析。而空间关系信息主要涉及几何关系的“相连”、“相邻”、“包含”等信息,它通常用拓扑关系或拓扑结构的方法来分析。拓扑关系是明确定的
|
相等(Equals):
|
几何形状拓扑上相等。
|
|
脱节(Disjoint):
|
几何形状没有共有的点。
|
|
相交(Intersects):
|
几何形状至少有一个共有点(区别于脱节)
|
|
接触(Touches):
|
几何形状有至少一个公共的边界点,但是没有内部点。
|
|
交叉(Crosses):
|
几何形状共享一些但不是所有的内部点。
|
|
内含(Within):
|
几何形状A的线都在几何形状B内部。
|
|
包含(Contains):
|
几何形状B的线都在几何形状A内部(区别于内含)
|
|
重叠(Overlaps):
|
几何形状共享一部分但不是所有的公共点,而且相交处有他们自己相同的区域。
|
下面的例子介绍了 equals、disjoint、intersects 的用法
-
package com.mapbar.geo.jts;
-
-
import org.geotools.geometry.jts.JTSFactoryFinder;
-
-
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Coordinate;
-
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Geometry;
-
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.GeometryFactory;
-
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.LineString;
-
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Point;
-
import com.vividsolutions.jts.io.ParseException;
-
import com.vividsolutions.jts.io.WKTReader;
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public class GeometryRelated {
-
-
private GeometryFactory geometryFactory = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory( null );
-
-
public Point createPoint(String lon,String lat){
-
Coordinate coord = new Coordinate(Double.parseDouble(lon), Double.parseDouble(lat));
-
Point point = geometryFactory.createPoint( coord );
-
return point;
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public boolean equalsGeo() throws ParseException{
-
WKTReader reader = new WKTReader( geometryFactory );
-
LineString geometry1 = (LineString) reader.read("LINESTRING(0 0, 2 0, 5 0)");
-
LineString geometry2 = (LineString) reader.read("LINESTRING(5 0, 0 0)");
-
-
-
-
return geometry1.equals(geometry2);
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public boolean disjointGeo() throws ParseException{
-
WKTReader reader = new WKTReader( geometryFactory );
-
LineString geometry1 = (LineString) reader.read("LINESTRING(0 0, 2 0, 5 0)");
-
LineString geometry2 = (LineString) reader.read("LINESTRING(0 1, 0 2)");
-
return geometry1.disjoint(geometry2);
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public boolean intersectsGeo() throws ParseException{
-
WKTReader reader = new WKTReader( geometryFactory );
-
LineString geometry1 = (LineString) reader.read("LINESTRING(0 0, 2 0, 5 0)");
-
LineString geometry2 = (LineString) reader.read("LINESTRING(0 0, 0 2)");
-
Geometry interPoint = geometry1.intersection(geometry2);
-
System.out.println(interPoint.toText());
-
return geometry1.intersects(geometry2);
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
-
GeometryRelated gr = new GeometryRelated();
-
System.out.println(gr.equalsGeo());
-
System.out.println(gr.disjointGeo());
-
System.out.println(gr.intersectsGeo());
-
}
-
-
}
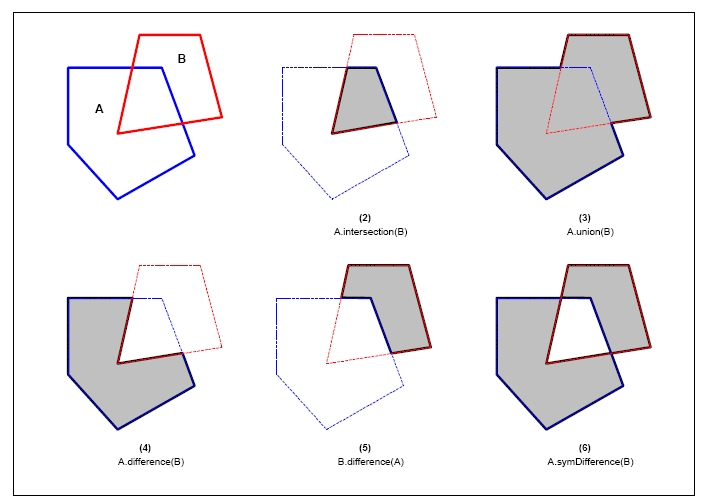
Geometry 叠加操作
|
缓冲区分析(Buffer)
|
包含所有的点在一个指定距离内的多边形和多多边形
|
|
凸壳分析(ConvexHull)
|
包含几何形体的所有点的最小凸壳多边形(外包多边形)
|
|
交叉分析(Intersection)
|
交叉操作就是多边形AB中所有共同点的集合。
|
|
联合分析(Union)
|
AB的联合操作就是AB所有点的集合。
|
|
差异分析(Difference)
|
AB形状的差异分析就是A里有B里没有的所有点的集合。
|
|
对称差异分析(SymDifference)
|
AB形状的对称差异分析就是位于A中或者B中但不同时在AB中的所有点的集合
|
在GIS中,缓冲(buffering)是一种用于计算包含在一个几何图形(Geometry)特定距离区域内所有点的的操作。在数学术语中,这被称为通过一个与缓冲区相等的圆的半径去计算几何图形的闵可夫斯基(Minkowski)总和。发现正的(positive)和负的(negative)缓冲,有时与操作的腐蚀(erosion)和膨胀(dilation)有关。在CAD/CAM,缓冲曲线被称为偏移曲线(offset
curves)。你可以使用JTS,通过Geometry buffer方法或者Bufferop类,去计算一个图形的缓冲区。缓冲操作所输入的Geometry可以是任何类别(包括任意的Geometry集合)。缓冲操作的结果通常是一种区域类型(area type)(多边形或者多多边形)。结果也可能为空[例如,一条线(linestring)的负缓冲。]
版权声明:本文来源CSDN,感谢博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 by-sa 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/omni360/article/details/44651781
站方申明:本站部分内容来自社区用户分享,若涉及侵权,请联系站方删除。



