社区微信群开通啦,扫一扫抢先加入社区官方微信群

社区微信群
社区微信群开通啦,扫一扫抢先加入社区官方微信群

社区微信群
for循环一般会访问一个可迭代的对象(如序列或者是迭代器),并且在所有条目都处理过之后结束循环。
for ivalue in (1,2,3)(迭代器):
print ivalue
每次循环, ivalue 迭代变量被设置为可迭代对象的当前元素。
for语句循环特点:
(1)通常用于遍历序列成员:字符串、列表、元组和字典;
(2)会自动的调用迭代器的next()方法,捕获StopIteration异常并结束循环;
通过序列项迭代
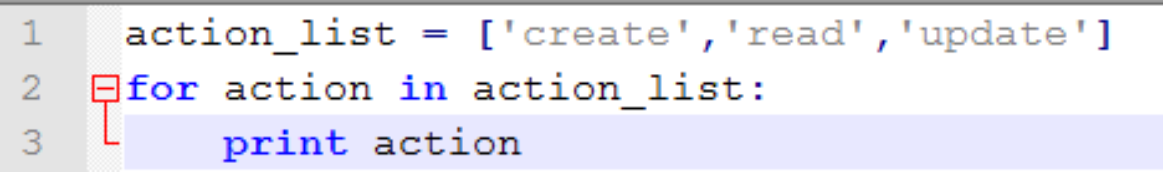
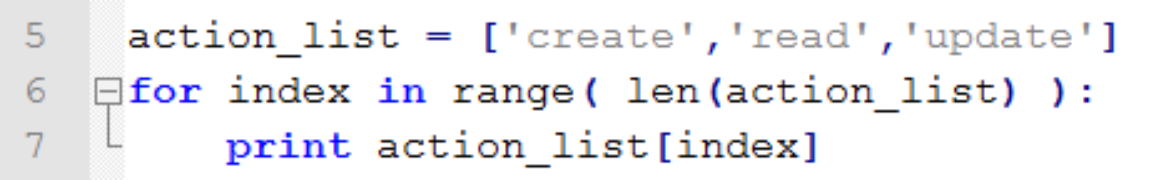
通过序列索引迭代
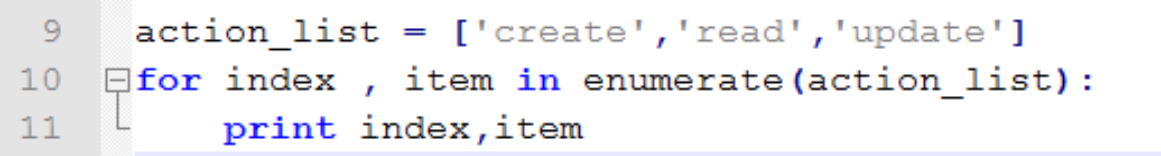
通过项和索引迭代
range( start , end, step = 1 )
range()会返回一个包含所有k的列表:
(1)start <= k < end
(2)k每次递增step,step不能为0,否则发送错误
range()简略用法:
range( end ) (start默认为0,step为1)
range( start , end )
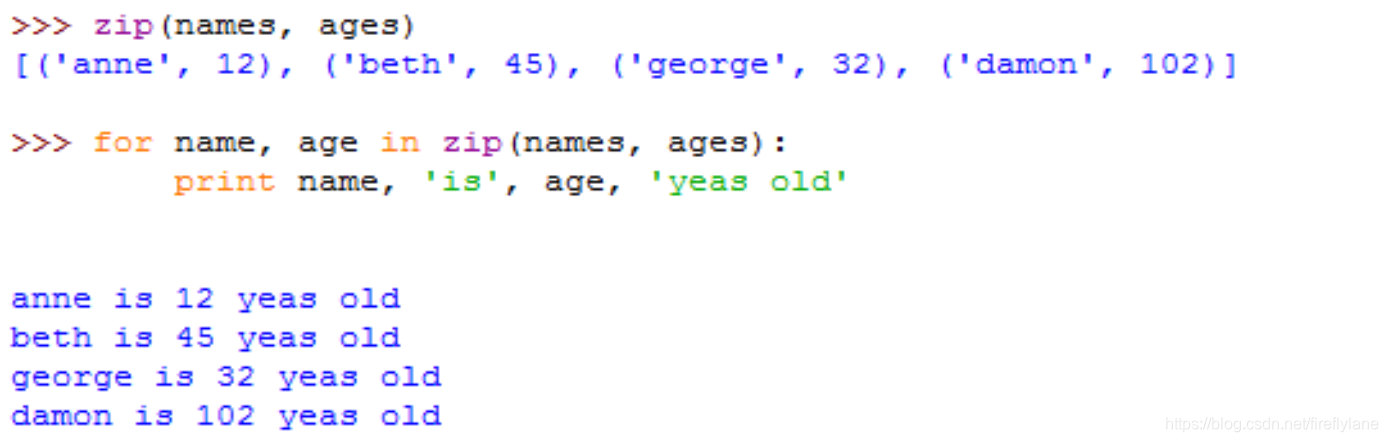
同时迭代两个序列
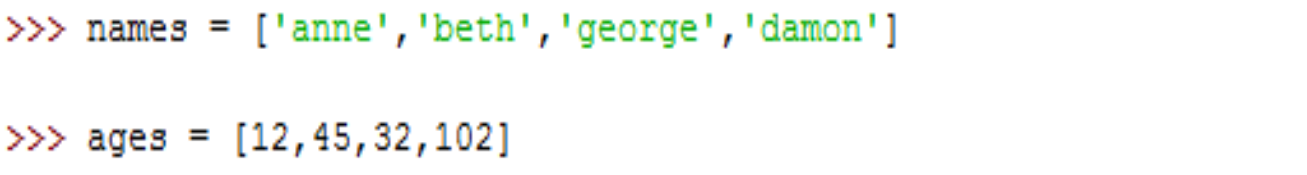
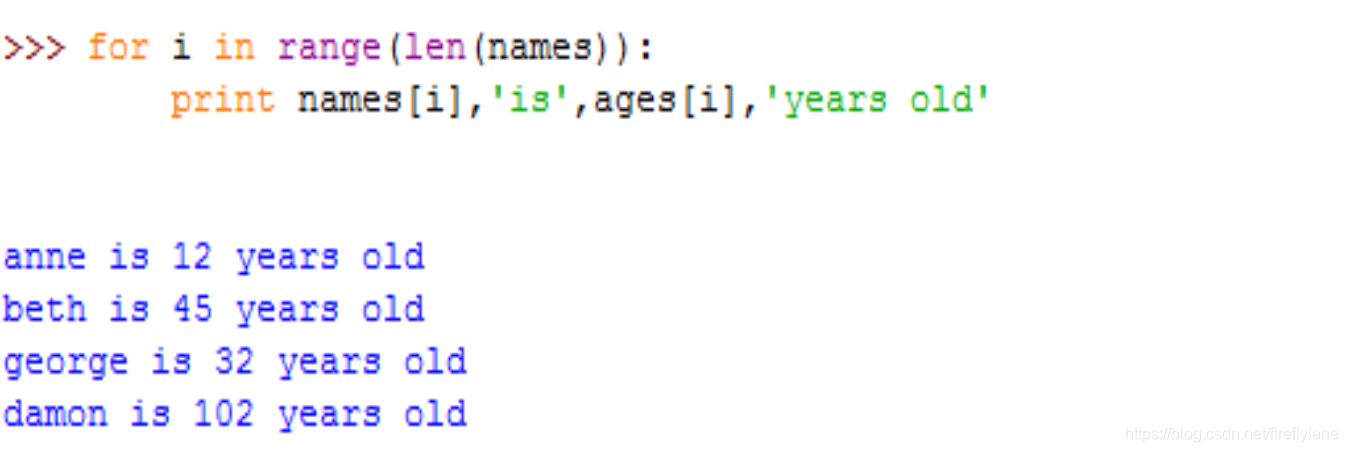
内建函数zip用来进行并行迭代,可用作多个序列(能够处理不等长,最短原则)

根据已有列表,高效创建新列表的方式。
列表解析是Python迭代机制的一种应用,它常用于实现创建新的列表,因此用在[]中。
[expression for iter_val in iterable]
[expression for iter_val in iterable if cond_expr]
要求:列出1~10中大于等于4的数字的平方
####################################################
1、普通方法:
>>> L = []
>>> for i in range(1,11):
... if i >= 4:
... L.append(i**2)
...
>>> print L
[16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100]
####################################################
2、列表解析
>>>L = [ i**2 for i in range(1,11) if i >= 4 ]
>>>print L
[16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100]
要求:列出"/var/log"中所有已'.log'结尾的文件
##################################################
1、普通方法
>>>import os
>>>file = []
>>> for file in os.listdir('/var/log'):
... if file.endswith('.log'):
... file.append(file)
...
>>> print file
['anaconda.ifcfg.log', 'Xorg.0.log', 'anaconda.storage.log', 'Xorg.9.log', 'yum.log', 'anaconda.log', 'dracut.log', 'pm-powersave.log', 'anaconda.yum.log', 'wpa_supplicant.log', 'boot.log', 'spice-vdagent.log', 'anaconda.program.log']
##################################################
2.列表解析
>>> import os
>>> file = [ file for file in os.listdir('/var/log') if file.endswith('.log') ]
>>> print file
['anaconda.ifcfg.log', 'Xorg.0.log', 'anaconda.storage.log', 'Xorg.9.log', 'yum.log', 'anaconda.log', 'dracut.log', 'pm-powersave.log', 'anaconda.yum.log', 'wpa_supplicant.log', 'boot.log', 'spice-vdagent.log', 'anaconda.program.log']
要求:实现两个列表中的元素逐一配对。
1、普通方法:
>>> L1 = ['x','y','z']
>>> L2 = [1,2,3]
>>> L3 = []
>>> for a in L1:
... for b in L2:
... L3.append((a,b))
...
>>> print L3
[('x', 1), ('x', 2), ('x', 3), ('y', 1), ('y', 2), ('y', 3), ('z', 1), ('z', 2), ('z', 3)]
####################################################
2、列表解析:
>>> L1 = ['x','y','z']
>>> L2 = [1,2,3]
L3 = [ (a,b) for a in L1 for b in L2 ]
>>> print L3
[('x', 1), ('x', 2), ('x', 3), ('y', 1), ('y', 2), ('y', 3), ('z', 1), ('z', 2), ('z', 3)]
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!
