社区微信群开通啦,扫一扫抢先加入社区官方微信群

社区微信群
社区微信群开通啦,扫一扫抢先加入社区官方微信群

社区微信群
摘要: 1.Java8 新特性介绍 2.项目中应用
原文链接 https://my.oschina.net/chenxiaobian/blog/704421,https://www.cnblogs.com/hmdrzql/p/6354010.html
现在我们有一个需求:给一个user组成的list 按照user的年龄排序。实现不难,代码如下:

UserCompare是一个实现了Comprator的类

这种方法由于sort方法的第二个参数是Comparator 所以你要写一个实现类(我这里是UserCompare类),并且override该接口的实现方法。
java8提供了lambda来简化,有了lambda程序员从此不加班呀~
![]()
刚才那个Comparator的实现类以及内部若干代码就都省了,代之以lambda表达式。
另外,IntelliJ会提示你改成更好的写法
![]()
实现类里有多少代码,你就省了多少行代码。
高兴了半天,到底是什么原理呢?其实是java8新提供的语法糖。
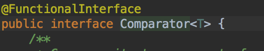
我们打开java1.8 Comparator的定义,发现了类定义上面多了一个@FunctionalInterface
对,1.8多了一个概念就是FunctionalInterface,这个Comparator就是一个FunctionalInterface
有了这个注解,原来使用实现类的地方就可以代之以lambda表达式。
Lambda表达式
函数式接口
Stream
Optional
Predicate
Function
Consumer
Filter
Map-Reduce
新的Date API
最核心的当然是函数式编程了,写代码非常简单,请看下面详细例子介绍
很多同学一开始接触Java8可能对Java8 Lambda表达式有点陌生,下面我将结合实例介绍Java8的使用 并与Java7进行比较:
基础类
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Person {
private int id;
private String name;
private String address;
}
public class ExampleList {
private static List<String> items = new ArrayList<>();
static {
items.add("A");
items.add("BC");
items.add("C");
items.add("BD");
items.add("E");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Java8之前操作List
for(String item:items){
System.out.println(item);
}
//Java8 lambda遍历list
items.forEach(c-> System.out.println(c));
items.forEach(item->{
if("C".equals(item)){
System.out.println(item);
}
});
System.out.println("--------");
//先过滤
items.stream().filter(s->s.contains("B")).forEach(c1-> System.out.println(c1));
}
}
public class ExampleMap {
private static Map<String, Integer> items = new HashMap<>();
static {
items.put("A", 10);
items.put("B", 20);
items.put("C", 30);
items.put("D", 40);
items.put("E", 50);
items.put("F", 60);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Java8之前遍历是这样遍历map
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry:items.entrySet()){
System.out.println("key:" + entry.getKey() + " value:" + entry.getValue());
}
//Java8遍历map
items.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println("key:" + key + " value:" + value));
}
}
/**
*
*Java8 Collectors.groupingBy and Collectors.mapping example
*/
public class ExampleMapping {
private static List<Person> personList = Lists.newArrayList();
static {
personList.add(Person.builder().id(10).address("apple").address("shanghai").build());
personList.add(Person.builder().id(12).address("apple").address("wuhan").build());
personList.add(Person.builder().id(16).address("apple").address("nanjing").build());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//分组
Map<String, List<Person>> collect = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(c -> c.getAddress()));
System.out.println(collect);
}
}
public class ExampleListConvertMap {
private static List<Person> personList = Lists.newArrayList();
static{
personList.add(Person.builder().id(20).name("zhangsan").address("shanghai").build());
personList.add(Person.builder().id(30).name("lisi").address("nanjing").build());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Java8 List转换Map
Map<Integer,Person> map_ = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap((key->key.getId()),(value->value)));
map_.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println(key + ":" + value));
Map<Integer, Person> mappedMovies = personList.stream().collect(
Collectors.toMap(Person::getRank, Person::getData));
}
}
public class ExampleFilterMap {
private static Map<Integer,String> map_ = Maps.newHashMap();
static{
map_.put(1, "linode.com");
map_.put(2, "heroku.com");
map_.put(3, "digitalocean.com");
map_.put(4, "aws.amazon.com");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//before java iterator map
String result = null;
for(Map.Entry<Integer,String> entry:map_.entrySet()){
if("heroku.com".equals(entry.getValue())){
result = entry.getValue();
}
}
System.out.println("Before Java 8 :" + result);
//Java8 Map->Stream->Filter->String
result = map_.entrySet().stream().
filter(map->"heroku.com".equals(map.getValue()))
.map(map->map.getValue())
.collect(Collectors.joining());
System.out.println("Java 8 :" + result);
Map<Integer,String> collect = map_.entrySet().stream()
.filter(c->c.getKey()==2)
.collect(Collectors.toMap(p->p.getKey(),p->p.getValue()));
System.out.println(collect);
}
}
Optional<String> optional = Optional.of("hello");
System.out.println(optional.isPresent());//true
System.out.println(optional.get());//hello
System.out.println(optional.orElse("false"));
optional.ifPresent((s)-> System.out.println(s.charAt(0)));//h
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Employee {
private String name;
private int salary;
private String office;
}
public class ExampleEmployee {
private static List<Employee> employeeList = Lists.newArrayList();
static{
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Matt").salary(5000).office("New York").build());
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Steve").salary(6000).office("London").build());
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Carrie").salary(20000).office("New York").build());
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Peter").salary(7000).office("New York").build());
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Pat").salary(8000).office("London").build());
employeeList.add(Employee.builder().name("Tammy").salary(29000).office("Shanghai").build());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//anyMatch
boolean isMatch = employeeList.stream().anyMatch(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("London"));
System.out.println(isMatch);
//返回所有salary大于6000
boolean matched = employeeList.stream().allMatch(employee -> employee.getSalary()>4000);
System.out.println(matched);
//找出工资最高
Optional<Employee> hightestSalary = employeeList.stream().max((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e1.getSalary(),e2.getSalary()));
System.out.println(hightestSalary);
//返回姓名列表
List<String> names = employeeList.stream().map(employee -> employee.getName()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(names);
//List转换成Map
Map<String,Employee> employeeMap = employeeList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap((key->key.getName()),(value->value)));
employeeMap.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println(key + "=" + value));
//统计办公室是New York的个数
long officeCount = employeeList.stream().filter(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("Shanghai")).count();
System.out.println(officeCount);
//List转换为Set
Set<String> officeSet = employeeList.stream().map(employee -> employee.getOffice()).distinct().collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(officeSet);
//查找办公室地点是New York的员工
Optional<Employee> allMatchedEmployees = employeeList.stream().filter(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("New York")).findAny();
System.out.println(allMatchedEmployees);
//按照工资的降序来列出员工信息
List<Employee> sortEmployeeList = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e2.getSalary(),e1.getSalary())).collect(Collectors.toList());
//按照名字的升序列出员工信息
List<Employee> sortEmployeeByName = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->e1.getName().compareTo(e2.getName())).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(sortEmployeeList);
System.out.println("按照名字的升序列出员工信息:" + sortEmployeeByName);
//获取工资最高的前2条员工信息
List<Employee> top2EmployeeList= employeeList.stream()
.sorted((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e2.getSalary(),e1.getSalary()))
.limit(2)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(top2EmployeeList);
//获取平均工资
OptionalDouble averageSalary = employeeList.stream().mapToInt(employee->employee.getSalary()).average();
System.out.println("平均工资:" + averageSalary);
//查找New York
OptionalDouble averageSalaryByOffice = employeeList.stream().filter(employee -> employee.getOffice()
.equals("New York"))
.mapToInt(employee->employee.getSalary())
.average();
System.out.println("New York办公室平均工资:" + averageSalaryByOffice);
}
}
public class EmployeeTest {
public static List<Employee> generateData() {
return Arrays.asList(new Employee("Matt", 5000, "New York"),
new Employee("Steve", 6000, "London"),
new Employee("Carrie", 10000, "New York"),
new Employee("Peter", 7000, "New York"),
new Employee("Alec", 6000, "London"),
new Employee("Sarah", 8000, "London"),
new Employee("Rebecca", 4000, "New York"),
new Employee("Pat", 20000, "New York"),
new Employee("Tammy", 9000, "New York"),
new Employee("Fred", 15000, "Tokyo"));
}
public static Map<String, Integer> generateMapData() {
Map<String, Integer> items = Maps.newHashMap();
items.put("A", 10);
items.put("B", 20);
items.put("C", 30);
items.put("D", 40);
items.put("E", 50);
items.put("F", 60);
return items;
}
@Test
public void testEmployee() {
List<Employee> results = generateData();
//打印出名字是Steve的员工信息
results.forEach(c -> {
if (c.getName().equals("Steve")) {
System.out.println(c);
}
});
System.out.println("---------");
//找出年薪超过6000的员工
results.stream().filter(c -> c.getSalary() >= 60000).forEach(c -> System.out.println(c));
System.out.println("--->>>>>>----");
//java8遍历map
Map<String, Integer> map_ = generateMapData();
map_.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println("key:" + key + "," + "value:" + value));
System.out.println("---->>>>分组>>>-----");
//java8 分组操作
Map<String, List<Employee>> groupMap = results.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(c -> c.getOffice()));
System.out.println(groupMap);
System.out.println("---->>>>List转化为Map>>>----");
//List转化Map
Map<String, Object> map = results.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Employee::getName, Employee::getOffice));
map.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println("key:" + key + "," + "value:" + value));
System.out.println("---->>>>>>>----");
Map<Integer, Employee> employeeMap = results.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap((key -> key.getSalary()), (value -> value)));
employeeMap.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + "," + value));
System.out.println("---->>遍历map>>>----");
//打印出值大于30的map
Map<String, Integer> resultMap = map_.entrySet().stream().filter(c -> c.getValue() > 30).collect(Collectors.toMap(p -> p.getKey(), p -> p.getValue()));
resultMap.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + "=" + value));
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
//打印key=D的map
Map<String, Integer> mapResults = map_.entrySet().stream().filter(c -> c.getKey().equals("D")).collect(Collectors.toMap(p -> p.getKey(), p -> p.getValue()));
mapResults.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + ">>>>" + value));
System.out.println(">>>>>>>Optional>>>>>>>");
Optional<String> optional = Optional.of("hello");
System.out.println(optional.isPresent());
}
@Test
public void testEmployeeExample() {
//anyMatch
List<Employee> employeeList = generateData();
boolean isMatch = employeeList.stream().anyMatch(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("London"));
System.out.println(isMatch);
//allMatch
boolean matched = employeeList.stream().allMatch(employee -> employee.getOffice().equals("London"));
System.out.println(matched);
//找出工资最高的
Optional<Employee> employeeOptional = employeeList.stream().max((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e1.getSalary(),e2.getSalary()));
System.out.println(employeeOptional);
//找出工资最少的
Optional<Employee> employee = employeeList.stream().min((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e1.getSalary(),e2.getSalary()));
System.out.println(employee);
//返回姓名列表
List<String> names = employeeList.stream().map(c->c.getName()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(names);
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>");
//List转化Map
Map<String,Employee> employeeMap = employeeList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap((key->key.getName()),(value->value)));
employeeMap.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println(key + "=" + value));
//统计办公室是New York的个数
long officeCount = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getOffice().equals("New York")).count();
System.out.println(officeCount);
long salaryCount = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getSalary()>60000).count();
System.out.println(salaryCount);
//List转化为Set
Set<String> officeSet = employeeList.stream().map(c->c.getOffice()).distinct().collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(officeSet);
Set<Integer> salarySet = employeeList.stream().map(c->c.getSalary()).distinct().collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(salarySet);
//查找办公室地点是New York的员工
Optional<Employee> optionals = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getOffice().equals("New York")).findAny();
System.out.println(optionals);
System.out.println(">>>>>工资降序排序>>>>>");
//按照工资的降序来列出员工信息
List<Employee> sortSalaryEmployeeList = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e2.getSalary(),e1.getSalary())).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(sortSalaryEmployeeList);
System.out.println(">>>>>姓名升序排序>>>>>");
List<Employee> sortNameEmployeeList = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->e1.getName().compareTo(e2.getName())).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(sortNameEmployeeList);
System.out.println(">>>>获取工资最高的前2条员工信息");
List<Employee> dispaly2EmployeeList = employeeList.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->Integer.compare(e2.getSalary(),e1.getSalary())).limit(2).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(dispaly2EmployeeList);
System.out.println(">>>>获取平均工资");
OptionalDouble averageSalary = employeeList.stream().mapToInt(c->c.getSalary()).average();
System.out.println(averageSalary);
System.out.println(">>>>获取工作地点的平均工资");
OptionalDouble optionalDouble = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getOffice().equals("New York")).mapToInt(c->c.getSalary()).average();
System.out.println(optionalDouble);
System.out.println(">>>>>>Java8 Optional用法>>>>>>");
Optional<String> stringOptional = Optional.of("test");
System.out.println(stringOptional.get());
Optional<String> isOptional = Optional.ofNullable("hello");
System.out.println(isOptional.isPresent());
System.out.println(isOptional.get());
System.out.println(isOptional.orElse("0"));
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>");
//Optional<String> optionalVal = Optional.of(null);
// System.out.println(optionalVal);
Optional<String> optional = Optional.ofNullable("optional");
System.out.println(optional);
System.out.println(optional.isPresent());
System.out.println(optional.get());
System.out.println(optional.orElse("haha"));
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>");
Optional<Employee> employeeOptional_ = employeeList.stream().filter(c->c.getOffice().equals("New York")).findFirst();
System.out.println(employeeOptional_);
}
如果觉得我的文章对您有用,请随意打赏。你的支持将鼓励我继续创作!
